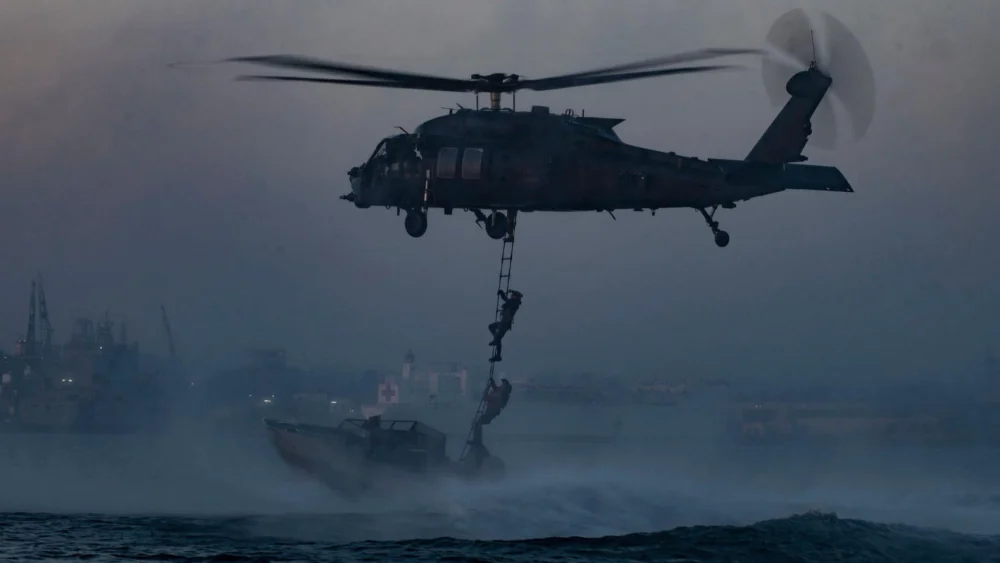
A significant re-evaluation of the indispensable role of military helicopters is currently underway across global defense forces, signaling a new era for these versatile aircraft as they reassert their strategic importance in a rapidly changing geopolitical landscape.
The historical perception of military helicopters as purely supplementary assets, often relegated to specific niche roles such as troop transport or close air support, is undergoing a profound transformation. This paradigm shift is driven by a confluence of technological advancements, evolving battlefield doctrines, and the persistent recognition of their unique capabilities in asymmetric warfare, contested environments, and rapid deployment scenarios. Once viewed by some as vulnerable relics susceptible to advanced air defenses, modern rotorcraft, augmented by cutting-edge avionics, weaponry, and operational concepts, are proving to be more resilient and strategically crucial than ever before.
A Legacy of Versatility, Rediscovered Strategic Imperative
For decades, the helicopter has been an iconic symbol of modern warfare, its distinctive thrumming blades a familiar soundtrack to conflicts ranging from Vietnam to Afghanistan. Initially conceived as tools for observation and transport, their combat potential was quickly realized, leading to the development of specialized attack helicopters like the AH-64 Apache and the Mi-24 Hind. These platforms provided unparalleled close air support, precision strike capabilities, and the ability to engage enemy armor and infantry with devastating effect. Beyond direct combat, their utility extended to vital logistical support, medical evacuation (MEDEVAC), reconnaissance, and special operations insertion and extraction.
However, the proliferation of sophisticated anti-access/area denial (A2/AD) systems, including advanced surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) and electronic warfare capabilities, led some analysts to question the long-term viability of low-flying rotorcraft in high-intensity conflict zones. This perception, coupled with the rise of unmanned aerial systems (UAS) offering similar reconnaissance and strike capabilities with reduced risk to personnel, contributed to a narrative that suggested a declining reliance on manned helicopters.
Contrary to this notion, recent operational deployments and strategic defense reviews are emphatically demonstrating the enduring and, in many ways, expanding relevance of military helicopters. The complex, multi-domain battlefields of the 21st century, characterized by hybrid threats, dispersed forces, and the need for rapid response, have inadvertently highlighted the specific advantages that manned rotorcraft offer.
Technological Advancements: Enhancing Survivability and Lethality
The resurgence of the war chopper is not merely a matter of strategic rediscovery; it is deeply intertwined with significant technological evolution. Modern helicopters are no longer simply agile platforms; they are increasingly sophisticated flying weapon systems.
-
Advanced Avionics and Sensor Suites: The integration of state-of-the-art sensor technology, including infrared imaging, advanced radar systems, and sophisticated electro-optical/infrared (EO/IR) turrets, grants pilots unprecedented situational awareness. This allows for superior target identification and tracking in all weather conditions and across vast operational areas, significantly enhancing both offensive and defensive capabilities. Helmet-mounted displays (HMDs) and integrated digital cockpits further streamline pilot workload and improve combat effectiveness.
-
Enhanced Survivability: To counter evolving threats, manufacturers have incorporated advanced defensive measures. These include improved radar warning receivers, missile approach warning systems, chaff and flare dispensers, and increasingly, directed energy countermeasures. Furthermore, advances in composite materials and airframe design contribute to greater resilience against battlefield damage. Some platforms are also being equipped with directed energy weapons, offering a glimpse into future defensive capabilities.
-
Lethal and Precision Munitions: The armament carried by modern helicopters has also seen substantial upgrades. Beyond traditional rockets and cannons, platforms are now equipped with advanced air-to-ground missiles (AGMs) offering extended ranges, precision guidance, and variable-yield warheads. This allows helicopters to engage targets from stand-off distances, increasing their survivability while maintaining a high degree of accuracy. The integration of smart munitions and loitering munitions capable of being deployed from helicopters further expands their offensive potential.
-
Network-Centric Warfare Integration: Helicopters are now fully integrated into the broader network-centric warfare architecture. This allows for seamless data sharing with other airborne and ground assets, enabling coordinated attacks, real-time intelligence dissemination, and dynamic re-tasking. The ability to act as mobile command and control nodes or communication relays further amplifies their strategic value.
Evolving Operational Doctrines: Adapting to Modern Challenges
The renewed emphasis on helicopters is also a reflection of evolving military thinking and the adaptation of operational doctrines to contemporary threats.
-
Asymmetric Warfare and Counter-Insurgency: In environments where adversaries employ dispersed, irregular tactics, helicopters offer a crucial advantage. Their ability to rapidly deploy forces into remote or difficult terrain, provide immediate fire support, and conduct persistent surveillance is invaluable for counter-insurgency operations and maintaining stability. MEDEVAC capabilities remain paramount, ensuring rapid medical attention for wounded personnel.
-
Contested Airspace and A2/AD Environments: While advanced air defenses pose a challenge, modern helicopter tactics are evolving to mitigate these risks. Low-level ingress and egress, terrain masking, sophisticated electronic warfare suites, and the use of decoys are employed to penetrate contested airspace. Furthermore, the ability of helicopters to operate in the "weasel" role – hunting enemy air defense systems – is increasingly recognized as a critical capability.
-
Rapid Global Mobility and Power Projection: Helicopters, particularly larger transport variants, play a vital role in rapid deployment and power projection. They enable forces to bypass heavily defended infrastructure, reach areas inaccessible by conventional means, and conduct immediate operationalization upon arrival. This agility is crucial for responding to crises and projecting influence in volatile regions.
-
Special Operations and Deep Strike: The unique stealth and precision insertion capabilities of specialized helicopters make them indispensable for special operations forces. They can infiltrate highly sensitive areas, conduct reconnaissance, and extract personnel with a minimal footprint, often operating under the cover of darkness or adverse weather. Larger attack helicopters can also be employed for deep strike missions against high-value targets, operating in conjunction with other strike assets.
-
Interoperability and Joint Operations: The modern battlefield demands seamless integration between different branches of service and allied forces. Helicopters are increasingly designed and operated with interoperability in mind, allowing for joint missions and the efficient sharing of resources and capabilities. This is particularly evident in multinational operations where diverse helicopter assets must function cohesively.
The Future of Rotorcraft: Unmanned Integration and Next-Generation Platforms
The future of military helicopters is not about replacing manned aircraft with unmanned systems, but rather about a synergistic integration. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are increasingly being deployed as escorts, reconnaissance partners, or even as weapons platforms that can extend the range and lethality of manned helicopters. This "manned-unmanned teaming" (MUM-T) allows manned helicopters to retain their tactical decision-making and command capabilities while leveraging the persistent surveillance and standoff attack potential of drones.
Furthermore, the development of next-generation helicopter platforms is already underway. These will likely incorporate:
- Advanced Rotorcraft Technologies: Concepts such as compound helicopters (with wings and pusher propellers for increased speed) and tiltrotor aircraft (like the V-22 Osprey) are pushing the boundaries of speed, range, and operational flexibility.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Autonomy: AI will play an increasing role in enhancing pilot assistance, optimizing flight paths, improving threat detection, and potentially enabling semi-autonomous or fully autonomous operations in certain scenarios.
- Directed Energy and Advanced Weaponry: The integration of directed energy weapons for defense and offense, along with even more sophisticated guided munitions, will further enhance the combat effectiveness of future rotorcraft.
- Stealth Technologies: While helicopters are inherently difficult to make truly stealthy, advancements in signature reduction (radar, infrared, acoustic) will continue to be a focus, particularly for specialized mission profiles.
Conclusion: A Vital Component of Modern Military Power
The narrative of the declining relevance of military helicopters has been definitively challenged and, in many respects, reversed. Through continuous technological innovation and strategic adaptation, rotorcraft have not only maintained their vital roles but have expanded them, proving to be indispensable assets in the complex and dynamic operational environments of the 21st century. Their unique combination of speed, agility, firepower, and versatility ensures their continued prominence as a cornerstone of modern military power, capable of projecting force, ensuring mobility, and providing critical support across the spectrum of conflict. The "war chopper" is not just returning; it is evolving into an even more potent and indispensable element of defense strategy.