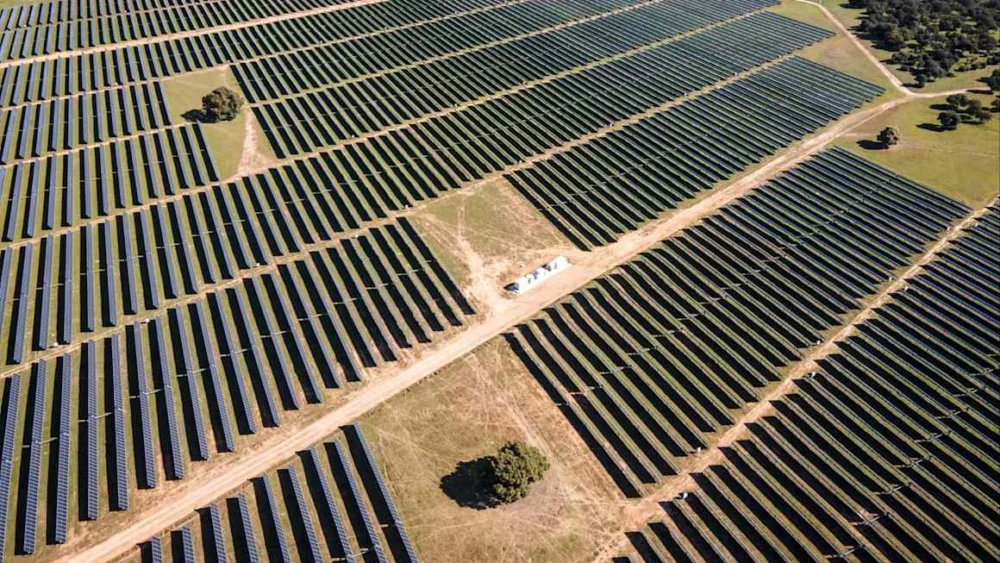
The burgeoning solar power capacity across Spain has led to an unprecedented surplus of electricity generation, particularly during peak daylight hours, resulting in significant price reductions in the wholesale energy market. This "discount season" for solar power is compelling plant operators and the broader industry to re-evaluate operational strategies and explore innovative solutions to maintain profitability and ensure grid stability.
The Unforeseen Bounty of Sunshine: A Market Disruption
Spain has emerged as a leading European nation in solar photovoltaic (PV) deployment, driven by a combination of favorable government policies, declining technology costs, and abundant solar resources. This rapid expansion has, however, created a new set of challenges. On many days, particularly during spring and summer, the sheer volume of solar electricity fed into the national grid overwhelms demand. This imbalance directly impacts wholesale electricity prices, pushing them to near-zero or even negative territory during periods of peak solar production.
This phenomenon, often referred to as "cannibalization," occurs when the increased supply of solar power drives down the marginal price of electricity. Generators with higher operational costs, such as older fossil fuel plants, are often forced offline, while even solar producers find their revenue streams significantly diminished. For solar power plants, which have substantial upfront capital costs, prolonged periods of ultra-low or negative prices can jeopardize their financial viability and the return on investment.
The implications extend beyond individual plant profitability. A consistently low price environment can discourage future investment in renewable energy projects, potentially slowing down Spain’s transition towards a fully decarbonized power sector. It also poses a challenge for grid operators who must manage the intermittency of solar generation and ensure a stable supply of electricity, even when solar output fluctuates.
Navigating the Sunshine Glut: Strategies for Adaptation
In response to this evolving market dynamic, various stakeholders are actively pursuing strategies to mitigate the effects of the solar surplus and unlock new value streams.
1. Enhanced Storage Solutions: The most direct countermeasure to solar oversupply is energy storage. Investing in battery energy storage systems (BESS) allows solar plant operators to capture excess electricity generated during peak sunshine hours and discharge it later when demand is high or solar output is low. This not only helps to smooth out the intermittency of solar power but also enables operators to sell stored energy at more favorable prices. While the initial investment in battery technology remains a significant consideration, the declining costs and increasing efficiency of BESS are making this an increasingly attractive proposition. Furthermore, grid-scale storage can provide valuable ancillary services, such as frequency regulation and voltage support, generating additional revenue streams.
2. Demand-Side Management and Flexibility: Shifting demand to align with periods of high solar generation is another crucial strategy. This involves incentivizing industrial consumers, electric vehicle charging infrastructure, and even residential users to consume electricity when it is abundant and cheap. Technologies such as smart grids, intelligent metering, and dynamic pricing mechanisms play a vital role in enabling this flexibility. For instance, large industrial facilities could be contracted to increase their energy consumption during midday periods in exchange for significantly discounted electricity rates. Similarly, smart charging algorithms for electric vehicles can be programmed to prioritize charging when solar output is at its peak.
3. Market Innovation and New Revenue Streams: The current market structure, primarily designed for dispatchable generation, is being challenged by the influx of variable renewable energy. Industry participants are exploring innovative market mechanisms that can better monetize the attributes of solar power and reward its flexibility. This includes:
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) with Price Floors: Long-term PPAs can provide revenue certainty for solar projects. However, with the current price volatility, incorporating price floors can offer a crucial safety net against prolonged periods of negative pricing.
- Ancillary Services Markets: Beyond direct electricity sales, solar plants equipped with inverters capable of providing grid services are increasingly participating in ancillary services markets. These services, essential for maintaining grid stability, can offer a stable and often lucrative revenue stream independent of wholesale energy prices.
- Green Hydrogen Production: The surplus of cheap renewable electricity presents a significant opportunity for green hydrogen production. Electrolyzers powered by solar energy can produce hydrogen with zero carbon emissions, creating a new market for this versatile energy carrier. Hydrogen can be stored, transported, and used in various sectors, including industry, transport, and potentially for power generation, thus providing a valuable outlet for excess solar power.
- Sector Coupling: Integrating the electricity sector with other energy-consuming sectors, such as heating and cooling, transportation, and industry, can create new demand for renewable electricity. For example, heat pumps can be used to store thermal energy when electricity is cheap, and electric vehicles can be charged during periods of high solar generation.
4. Geographical Diversification and Interconnection: While Spain benefits from abundant solar resources, the oversupply is often localized and temporal. Enhancing interconnections with neighboring countries can help export surplus electricity to regions with higher demand or lower solar availability, thereby balancing the market and improving overall system efficiency. This requires significant investment in transmission infrastructure and cross-border market integration.
Expert Perspectives and Future Outlook
Industry analysts and energy economists emphasize that the current situation, while presenting challenges, is a natural consequence of successful renewable energy deployment. Dr. Elena Rodríguez, a senior energy market analyst, commented, "Spain’s solar success is a testament to its commitment to decarbonization. The challenge now is to adapt our energy systems and market frameworks to fully harness this abundant, clean resource. The key lies in embracing flexibility, innovation, and smart integration."
The long-term outlook suggests that the trend of solar power surplus is likely to continue and potentially intensify as more capacity comes online. This will necessitate a fundamental shift in how electricity markets are designed and operated. Future market reforms may need to incorporate mechanisms that better value the grid services provided by renewables, incentivize demand flexibility, and facilitate the integration of storage and other enabling technologies.
Furthermore, the development of robust carbon pricing mechanisms and the increasing demand for green products and services globally will likely create new economic incentives for renewable energy. The ability of solar power plants to provide not only electricity but also decarbonization solutions for other sectors, such as hydrogen production, will be crucial for their sustained profitability.
The "discount season" for Spanish solar power is not an endpoint but a pivotal moment, signaling the need for a more sophisticated and adaptable energy ecosystem. By proactively implementing innovative solutions, fostering market reforms, and embracing new technological advancements, Spain can transform this apparent challenge into an opportunity to solidify its position as a leader in the global energy transition, ensuring a sustainable and prosperous future powered by the sun. The ongoing evolution of the Spanish electricity market in response to its solar bounty will serve as a crucial case study for other nations embarking on similar renewable energy pathways.