OpenAI is significantly advancing the paradigm of web interaction with its Chromium-based Atlas browser, a sophisticated platform seamlessly integrating large language model capabilities directly into the browsing experience. This innovative browser is currently undergoing testing for a transformative new feature tentatively named "Actions," alongside demonstrating an impressive capacity for real-time video content analysis, exemplified by its ability to generate precise timestamps for online videos. Atlas redefines digital engagement by embedding artificial intelligence as an intrinsic component of user navigation, moving beyond conventional browsing to offer a deeply contextual and proactively intelligent assistant.
The fundamental premise of the ChatGPT Atlas browser diverges sharply from traditional web browsers by eliminating the operational friction typically associated with utilizing AI tools. Instead of the cumbersome process of switching between browser tabs, copying URLs, or extracting screenshots to input into a separate AI interface, Atlas centralizes this interaction. Users can now pose queries, seek clarifications, or request assistance directly within the active webpage, fostering an uninterrupted workflow. This inherent integration allows the AI to maintain a constant awareness of the user’s current context, enabling it to offer pertinent research support, elaborate on complex subjects, and execute multi-step tasks without requiring users to leave their current view.
A pivotal element distinguishing Atlas is its capacity for deep contextual understanding. The browser can interpret the visual and textual content displayed on a page, serving as an intelligent co-pilot for various online activities. Whether a user is conducting in-depth research, seeking explanations for intricate concepts, or aiming to complete specific online tasks, Atlas stands ready to assist. This goes beyond simple search; it involves an active comprehension of the user’s immediate intent and the digital environment they are engaging with. This capability positions Atlas not merely as a tool for accessing information, but as a dynamic partner in knowledge acquisition and task execution.
Further enhancing its intelligence, Atlas incorporates a feature referred to as "browser memories." When activated, this functionality allows the browser to retain and recall relevant details from previously visited websites. This persistent memory is invaluable for tasks requiring comparison or long-term tracking, such as evaluating multiple job postings, comparing product specifications, or recalling research points across different sessions. The ability to automatically retrieve and present pertinent historical data significantly streamlines complex online activities, reducing cognitive load and enhancing efficiency. This proactive recall mechanism underscores Atlas’s ambition to transform the browser from a passive display mechanism into an active participant in the user’s digital journey.
Complementing its contextual awareness and memory functions is the introduction of an "agent mode." This sophisticated feature empowers Atlas to autonomously open new tabs and navigate through predefined or user-initiated workflows. For instance, it could be tasked with comparing prices across e-commerce sites, filling out forms, or aggregating information from multiple sources. OpenAI has underscored a commitment to user safety and security with this mode, implementing stringent limits and exercising heightened caution, particularly when interacting with sensitive websites or personal data. This controlled autonomy represents a significant leap towards truly intelligent agents capable of performing complex web-based operations on behalf of the user, yet with critical safeguards in place.
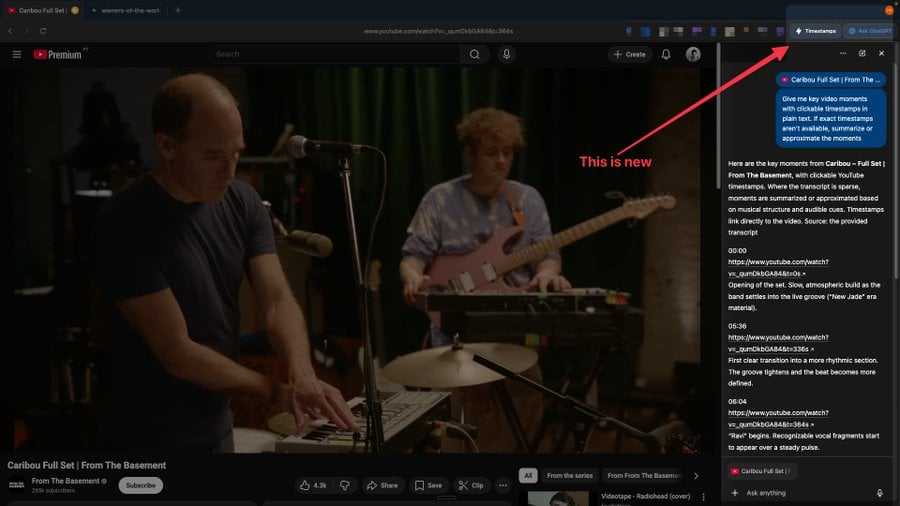
Recent observations by users on social media platforms, specifically X (formerly Twitter), have highlighted Atlas’s burgeoning ability to comprehend video content. Most notably, the browser has demonstrated proficiency in analyzing YouTube videos, with some users reporting the appearance of a "Timestamps" button. This functionality allows the integrated AI to extract and present a chronological list of key moments within a video, effectively creating an intelligent summary or navigation guide. This development signifies a major step in the AI’s multimodal understanding, extending its interpretive capabilities beyond text and static images to dynamic media, thereby enriching the user experience for learning, research, and entertainment consumption. The ability to automatically generate precise timestamps streamlines content review, enabling users to quickly locate relevant sections of lengthy videos without manual scrubbing.

OpenAI’s official release notes further corroborate ongoing developments, confirming a recent update focused predominantly on enhancing the browser’s stability and refining the overall day-to-day user experience. Key improvements include the resolution of a bug that could lead to excessive memory consumption, ensuring smoother performance. Additionally, the update introduces more intelligent and contextually relevant "what to ask next" suggestions, even when the Ask ChatGPT sidebar is not actively displayed. This proactive prompting anticipates user needs, guiding them towards more effective interaction with the AI.
Beyond core AI functionalities, OpenAI has implemented numerous quality-of-life upgrades across various aspects of the browser’s interface and performance. The tab management system has seen refinements, with the "Tab Search" feature now displaying the five most recently accessed tabs when empty, improving accessibility and navigation. Furthermore, a convenient keyboard shortcut, Cmd+K (or Ctrl+K on Windows), has been integrated to instantly trigger the tab search function, streamlining workflow for power users. These iterative enhancements reflect a dedication to creating a robust, user-friendly, and highly efficient browsing environment.
Looking ahead, OpenAI has publicly announced its intention to expand the availability of Atlas to Windows 11, indicating a strategic move to broaden its user base and establish a stronger foothold in the mainstream operating system market. This planned expansion underscores OpenAI’s vision for Atlas to become a widely adopted tool, bringing its unique blend of AI-powered browsing to a larger audience.
The Evolving Landscape of AI-Integrated Browsing
OpenAI’s foray into the browser market with Atlas is not an isolated incident but rather a significant move within a burgeoning trend towards AI-native web experiences. Several established browser developers and innovative startups are also experimenting with or have already integrated AI features into their platforms. Browsers like Arc have introduced novel ways to organize tabs and manage information, while others such as Brave and Opera have incorporated AI chatbots or summarization tools. Atlas distinguishes itself by deeply embedding ChatGPT, not just as an add-on, but as an integral part of the browser’s core functionality, designed to understand and interact with the web content itself. This fundamental integration aims to move beyond superficial AI assistance to a truly intelligent co-pilot for all online activities.
OpenAI’s strategic rationale behind developing a browser is multifaceted. Firstly, it provides a direct conduit for users to interact with their advanced AI models in a controlled environment, ensuring optimal performance and user experience. Secondly, it allows OpenAI to gather invaluable data on how users interact with AI in a browsing context, which can be critical for further model refinement and development. Thirdly, a proprietary browser offers a platform for potential monetization strategies, whether through premium features, integrated services, or future partnerships, without relying solely on API access or external platforms. Finally, by controlling the browser, OpenAI can dictate the terms of AI integration, potentially setting new industry standards for privacy, security, and ethical AI deployment in web environments.

The technical challenges in integrating a sophisticated AI model directly into a browser are considerable. It requires seamless interaction between the AI’s neural networks and the browser’s rendering engine, JavaScript execution, and network stack. The AI must be able to process visual layouts, understand dynamic content, and execute actions with minimal latency, all while maintaining system stability and security. The development of "Actions" and "Agent Mode" necessitates robust semantic understanding and the ability to parse complex web elements, identifying actionable components and predicting user intent with high accuracy. This represents a significant engineering feat, pushing the boundaries of what is technically feasible in browser design.
Implications for Productivity and User Experience
The advent of AI-native browsers like Atlas holds profound implications for personal and professional productivity. For researchers, the ability to have an AI summarize articles, compare data points across multiple tabs, or even structure research outlines automatically could dramatically accelerate their work. Students could benefit from real-time explanations of complex topics encountered on academic websites or personalized summaries of lectures available online. Professionals could leverage the agent mode to automate routine data entry, aggregate market information, or streamline administrative tasks, freeing up valuable time for higher-level strategic thinking.
The shift from a reactive browser, which merely displays content, to a proactive, intelligent browser capable of understanding, summarizing, and acting on information represents a fundamental change in the human-computer interaction paradigm. Users will no longer be solely responsible for navigating, processing, and synthesizing information; the browser itself will become an active participant in these cognitive tasks. This could lead to a significant reduction in digital fatigue and an overall enhancement of the online experience, making the web more accessible and efficient for a broader range of users.
Privacy, Security, and Ethical Considerations
The deep integration of AI into a browser, particularly with features like "browser memories" and "agent mode," inevitably raises critical questions regarding user privacy and data security. An AI with comprehensive access to a user’s browsing history, visited sites, and interaction patterns possesses an unprecedented level of insight into their digital life. OpenAI’s emphasis on "safety limits and extra caution on sensitive sites" for agent mode is a crucial acknowledgment of these concerns. However, the exact mechanisms for data anonymization, consent management, and the protection of sensitive information will be paramount for user trust and widespread adoption.
Ethical considerations also come into play with autonomous "agent mode." The ability for an AI to open tabs, click through workflows, and potentially interact with online services on behalf of a user necessitates clear boundaries and robust oversight. Questions arise regarding accountability in cases of unintended actions, potential for manipulation, or the propagation of misinformation if the AI’s understanding is flawed. OpenAI, as a leader in AI development, faces the responsibility of pioneering these ethical frameworks in parallel with technological advancement, ensuring that convenience does not come at the expense of user autonomy or digital safety. The transparent development and communication of these policies will be crucial for building a responsible AI-powered browsing future.
The Future Outlook for Web Browsing
OpenAI’s Atlas browser represents a significant milestone in the evolution of web interaction, pushing the boundaries of what a browser can achieve. Its integration of advanced AI capabilities, from contextual understanding and memory retention to video analysis and autonomous actions, signals a future where the web is not just navigated but intelligently assisted. As OpenAI continues to refine these features and expands its reach to platforms like Windows 11, the competitive landscape for web browsers is set for a dramatic transformation. Traditional browser vendors will likely be compelled to accelerate their own AI integration efforts to remain relevant.
Ultimately, Atlas could pave the way for a new standard in web browsing, where AI is not an optional add-on but an indispensable component that fundamentally enhances productivity, learning, and engagement. The success of Atlas will hinge on its ability to balance innovative functionality with robust security, privacy, and ethical considerations, setting a precedent for how AI can be integrated responsibly into the very fabric of our digital lives. The future of the web, as envisioned by Atlas, is one where the browser is not just a window to information, but an intelligent agent actively assisting in its comprehension and utilization.








