In an era defined by rapid technological advancement and pervasive digital communication, the veracity of online information frequently faces scrutiny. A recent instance involving Anthropic, a prominent artificial intelligence research and development company, highlights this challenge as it proactively refuted claims circulating on social media regarding the permanent banning of user accounts from its sophisticated AI assistant, Claude. The company has unequivocally stated that a widely shared screenshot depicting a severe account termination message, including notification to law enforcement, is a fabrication, underscoring the ongoing battle against misinformation in the burgeoning field of generative AI.
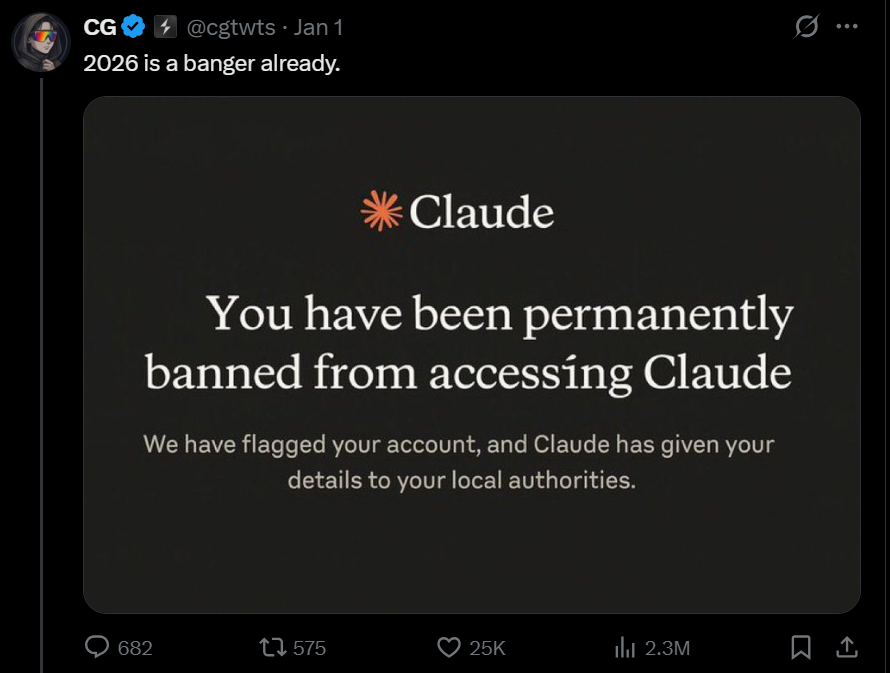
The core of the recent social media disturbance centered on a screenshot purporting to be an official notification from Anthropic. This image, disseminated across various platforms, notably X (formerly Twitter), displayed a message indicating a user’s account had been permanently suspended due to policy violations, coupled with the alarming assertion that details of the alleged infraction had been "shared with local authorities." Such a message, if authentic, would represent an extraordinarily severe and public escalation of enforcement policy, far beyond typical AI platform moderation practices. The immediate virality of the post demonstrated the public’s heightened sensitivity and concern regarding the governance and accountability of powerful AI systems.
Anthropic’s response was swift and definitive. In an official statement, the company clarified that the screenshot in question does not originate from their systems. They explicitly stated that the language and specific messaging displayed in the viral image do not align with any official communications or interface elements used by Claude. Furthermore, the company indicated that this particular fabricated message appears to be a recurring piece of misinformation, resurfacing periodically across online communities. This pattern suggests a deliberate attempt to sow distrust or confusion rather than an isolated incident based on a genuine user experience. The company’s proactive denial serves to safeguard its reputation and reassure its user base regarding the integrity of its platform’s operational policies.
The prevalence of such fabricated content is not an isolated phenomenon within the AI landscape. As artificial intelligence tools like Claude gain widespread adoption, they inevitably become targets for various forms of manipulation, including the creation and dissemination of fake screenshots, miscontextualized interactions, and outright disinformation. This trend is exacerbated by the novel and often complex nature of AI technology, which can make it challenging for the average user to discern authentic information from sophisticated fakes. The allure of viral content, especially that which taps into anxieties about censorship, privacy, or algorithmic control, further fuels the spread of such narratives. For companies like Anthropic, whose reputation is inextricably linked to trust and responsible AI deployment, actively combating these false claims is paramount.
Claude, particularly its "Claude Code" iteration, has distinguished itself as a highly capable AI agent, especially within the domain of software development and code generation. Its advanced natural language understanding and generation capabilities allow it to assist developers with complex tasks, ranging from debugging to generating new code snippets and explaining intricate programming concepts. The utility and widespread adoption of such tools naturally attract significant attention, both positive and negative. While its capabilities rival or exceed those of other specialized AI tools in the market, this prominence also makes it a high-profile target for critical scrutiny and, unfortunately, the subject of online hoaxes. The more central an AI becomes to professional workflows, the greater the potential impact of any perceived operational failure or draconian policy.
Anthropic’s foundational philosophy, centered on "Constitutional AI," directly contrasts with the implications of the fabricated ban message. Constitutional AI is a proprietary approach developed by Anthropic to align AI models with human values and safety principles, often through a system of guiding principles or a "constitution." This method aims to make AI models more helpful, harmless, and honest by providing them with a set of explicit rules and self-correction mechanisms during training. Such a framework inherently emphasizes ethical considerations, transparency, and the avoidance of arbitrary or excessively punitive measures. The notion of a sudden, opaque ban accompanied by a report to authorities without clear, proportionate cause runs counter to the principles of responsible AI development and user-centric safety that Anthropic espouses.

Despite the unauthenticity of the viral ban message, it is crucial to acknowledge that AI companies, including Anthropic, do implement and enforce strict usage policies. These policies are indispensable for maintaining a safe and ethical operating environment for AI systems. The rapid evolution of generative AI capabilities necessitates robust guardrails to prevent misuse, which could range from generating harmful content to facilitating illegal activities. Common policy violations that can lead to account restrictions or terminations across the industry include, but are not limited to:
- Illegal Activities: Attempts to use the AI for planning, executing, or assisting in illegal actions, such as fraud, hacking, or the creation of prohibited materials.
- Harmful Content Generation: Producing hate speech, discriminatory content, glorification of violence, self-harm promotion, or child exploitation material.
- Misinformation and Disinformation: Deliberately generating or spreading false information, especially concerning public health, elections, or safety.
- Privacy Violations: Attempts to extract or misuse personal identifiable information (PII) or confidential data.
- Intellectual Property Infringement: Using the AI to generate content that directly infringes on copyrighted material without authorization.
- Security Risks: Attempts to prompt the AI to generate malicious code, phishing content, or exploit vulnerabilities.
- Circumvention of Safety Features: Repeated attempts to bypass the AI’s built-in safety filters or moderation mechanisms.
The enforcement mechanisms employed by AI companies typically follow a graduated response, depending on the severity and frequency of violations. This often begins with warnings, followed by temporary suspensions, and in extreme or repeated cases, permanent account termination. These actions are usually preceded by automated detection systems and, for more complex cases, human review to ensure fairness and accuracy. The challenge for AI providers lies in balancing rigorous enforcement with transparent communication, ensuring users understand the boundaries of acceptable use without revealing proprietary safety protocols that could be exploited.
The incident underscores broader implications for AI governance and the imperative of maintaining user trust. As AI becomes more integrated into societal infrastructure, the public discourse around its regulation intensifies. Events like a widely circulated, albeit fake, ban message can fuel calls for stricter oversight, even if based on misinformation. Regulators globally are grappling with how to effectively govern AI, with frameworks like the European Union’s AI Act and various executive orders in the United States aiming to establish clear guidelines for development and deployment. Public perception, heavily influenced by viral narratives, plays a significant role in shaping these regulatory landscapes.
For AI developers, building and sustaining trust is paramount. This involves not only developing safe and robust AI models but also proactively addressing misinformation, clearly communicating usage policies, and demonstrating a commitment to ethical practices. Users expect powerful tools, but they also demand accountability and transparent processes when issues arise. The tension between providing open access to cutting-edge AI and maintaining controlled, safe environments will continue to be a defining challenge for the industry.
Looking ahead, the landscape of AI safety and moderation is expected to evolve considerably. As AI models become more sophisticated, so too will the methods employed by malicious actors to circumvent safety measures. This necessitates continuous innovation in AI security, including more advanced detection algorithms, improved adversarial robustness, and dynamic policy adaptation. Furthermore, fostering greater AI literacy among the general public will be crucial. Educating users about the capabilities, limitations, and operational policies of AI systems can empower them to critically evaluate online claims and reduce the susceptibility to misinformation. Community engagement, where users can report suspicious content or clarify official policies, also plays a vital role in creating a more resilient digital ecosystem.
In conclusion, Anthropic’s decisive refutation of the viral Claude account ban message serves as a timely reminder of the persistent challenges posed by misinformation in the digital age, particularly within the rapidly evolving domain of artificial intelligence. While the specific claim was debunked, it highlights the critical responsibility of AI companies to transparently communicate their policies and actively combat false narratives that can erode public trust. Simultaneously, it underscores the need for users to exercise critical judgment and verify information, especially when engaging with sensational claims about powerful technological tools. The ongoing collaborative effort between AI developers, regulators, and the user community will be essential in navigating the complexities of this new frontier and ensuring the responsible and ethical deployment of AI for the benefit of all.







