A high-stakes campaign employing voice phishing (vishing) techniques to compromise single sign-on (SSO) accounts across leading enterprise platforms, including Okta, Microsoft Entra, and Google, has been publicly claimed by the notorious cybercrime syndicate known as ShinyHunters, leading to widespread data theft and subsequent extortion attempts against affected organizations.
The digital threat landscape is perpetually reshaped by evolving attack methodologies and the persistent ingenuity of malicious actors. In a recent and concerning development, the cybercriminal group ShinyHunters has asserted responsibility for a series of highly effective social engineering attacks. These operations specifically target the robust authentication mechanisms of corporate SSO systems, which serve as critical gateways to an organization’s entire suite of cloud-based applications and proprietary data. The group’s declaration underscores a significant escalation in their operational sophistication, moving beyond conventional data breaches to exploit human vulnerabilities through meticulously crafted vishing schemes. This strategic shift highlights a growing trend among advanced persistent threat (APT) groups and financially motivated cybercriminals to leverage complex social engineering as a primary vector for initial access and subsequent data exfiltration.
The Evolution of ShinyHunters: A Persistent Threat Actor
ShinyHunters first emerged on the cybercrime scene with a reputation for large-scale data breaches, often acquiring vast databases from compromised companies and then selling this sensitive information on dark web marketplaces. Their early activities were characterized by opportunistic exploitation of misconfigurations, unpatched vulnerabilities, and insider threats. Over time, the group demonstrated an adaptive nature, integrating data extortion into their business model, leveraging the threat of public data leaks to coerce payments from victims. The current attribution of vishing attacks against SSO infrastructure marks a significant evolution in their tactics, indicating a move towards more active and interactive forms of social engineering, requiring substantial operational planning and real-time engagement. This progression places them among the more dangerous and versatile cybercriminal entities operating today, capable of executing multi-stage attacks that blend technical prowess with psychological manipulation. Their sustained activity and consistent ability to penetrate diverse corporate networks underscore a persistent threat that demands heightened vigilance from the cybersecurity community.

Understanding Single Sign-On (SSO) and Its Criticality
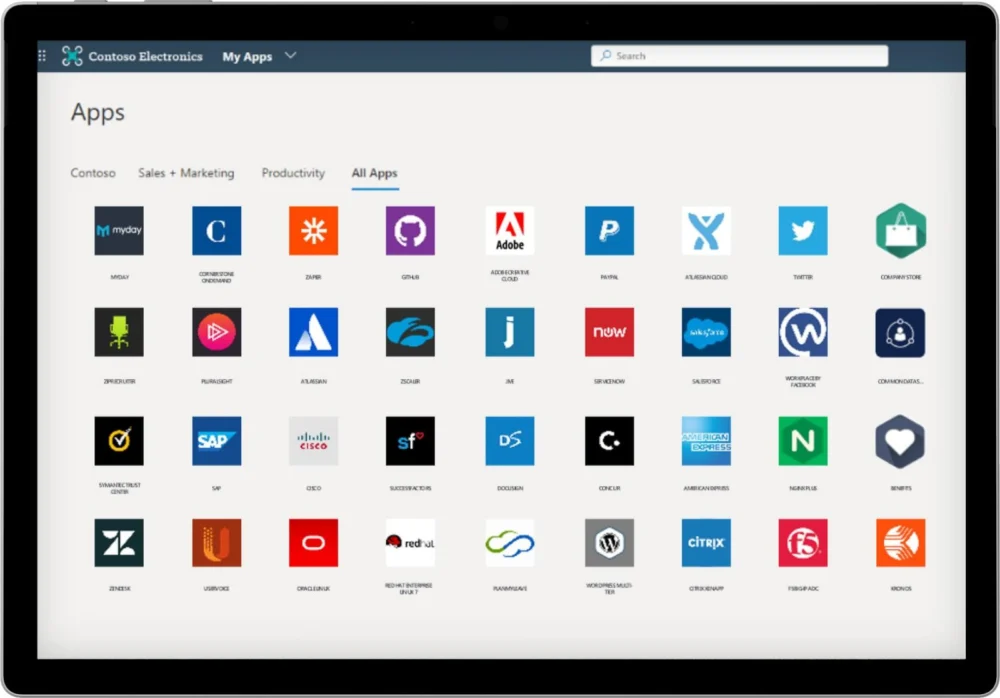
Single Sign-On (SSO) technology represents a cornerstone of modern enterprise IT infrastructure, designed to streamline user authentication and enhance productivity. By allowing users to access multiple applications and services with a single set of credentials, SSO platforms from providers like Okta, Microsoft Entra (formerly Azure AD), and Google Workspace significantly simplify the user experience and reduce password fatigue. From a security perspective, SSO centralizes authentication management, theoretically offering a more secure and manageable environment than disparate login systems. However, this centralization also introduces a critical single point of failure. A compromise of an SSO account grants attackers a "master key" to an extensive array of connected enterprise applications, including CRM systems like Salesforce, productivity suites such as Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace, collaboration tools like Slack, cloud storage services like Dropbox, and various other business-critical platforms from vendors like Adobe, SAP, Zendesk, and Atlassian. The interconnected nature of these platforms means that once an attacker gains access through a compromised SSO session, lateral movement across an organization’s digital ecosystem becomes significantly easier, enabling extensive data reconnaissance and exfiltration. This inherent vulnerability, while balanced against the operational benefits, necessitates robust protective measures around SSO accounts.
The Anatomy of the Vishing Attack: Social Engineering at its Core
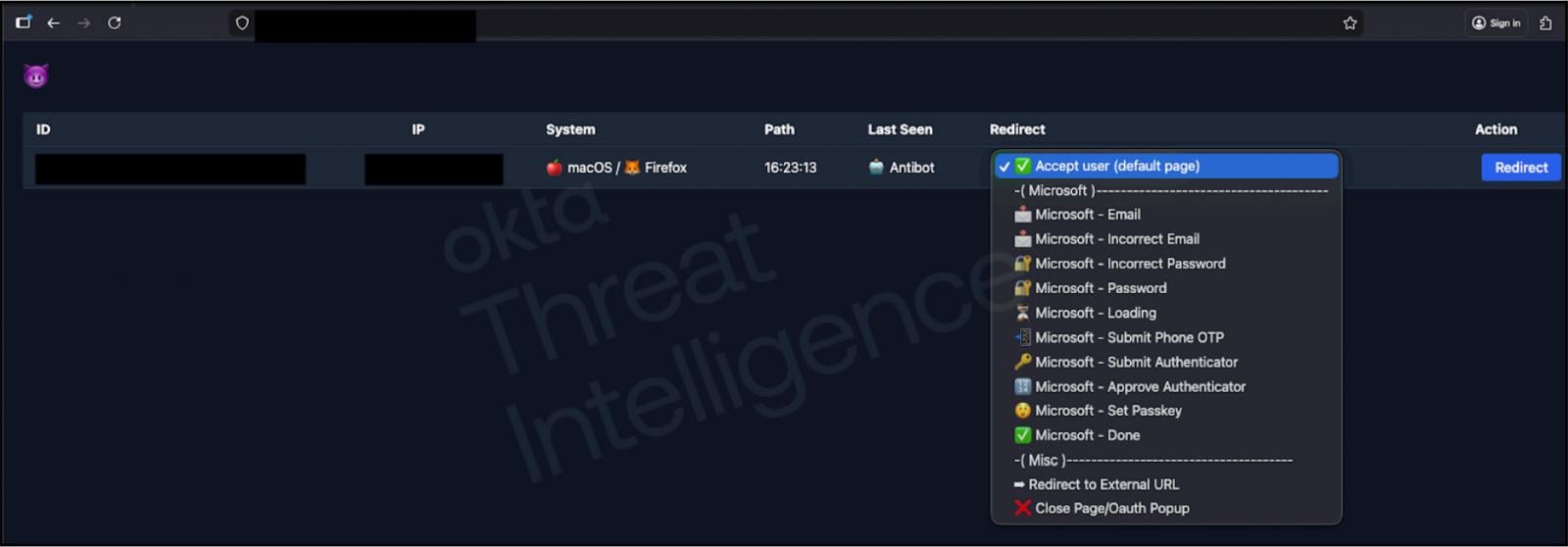
The attacks attributed to ShinyHunters meticulously exploit human trust and leverage sophisticated social engineering tactics. The core methodology involves "vishing," or voice phishing, where threat actors impersonate legitimate IT support personnel. This impersonation is often bolstered by pre-existing knowledge about the target employee and their organization, likely gleaned from publicly available information or previously stolen data. Attackers initiate calls to employees, creating a sense of urgency or concern about a supposed security issue or system upgrade. They guide victims to seemingly legitimate, but in fact fraudulent, login pages meticulously crafted to mimic the company’s authentic SSO portal.
The real-time interaction inherent in vishing is what distinguishes these attacks from traditional phishing emails. During the call, attackers instruct employees to enter their credentials and, crucially, their multi-factor authentication (MFA) codes or approve push notifications. The sophistication extends to dynamically changing elements on the phishing site in response to the victim’s actions and the real-time authentication flow on the legitimate service. This allows attackers to bypass even robust MFA mechanisms by tricking the user into unknowingly providing the second factor directly to the attacker, who then uses it immediately to log into the actual corporate system. The psychological pressure exerted during the call, combined with the convincing impersonation and tailored phishing sites, significantly diminishes an employee’s ability to detect the deception, making these attacks exceptionally potent.

Advanced Phishing Kits and Real-time MFA Bypass
The technical sophistication underpinning these vishing campaigns is noteworthy. Okta’s recent threat intelligence report, which aligns with observations from affected organizations, detailed the use of advanced phishing kits equipped with web-based control panels. These kits empower attackers to manipulate the victim’s view of the phishing site dynamically, synchronizing the deceptive interface with the ongoing phone conversation. For instance, if the attackers input stolen credentials into the genuine SSO service and are prompted for an MFA challenge, the phishing kit can instantaneously display a corresponding dialog box on the victim’s screen. This prompts the victim to approve a push notification, enter a Time-based One-Time Password (TOTP) code, or perform another authentication step, effectively relaying the MFA challenge directly to the attacker in real-time.
This real-time interaction and dynamic content generation are critical for bypassing modern MFA solutions. Traditional MFA methods, while effective against automated credential stuffing, are vulnerable to such interactive social engineering. The attacker acts as a man-in-the-middle, relaying authentication requests between the victim and the legitimate service. This advanced capability transforms a static phishing attempt into a dynamic, interactive session that is incredibly difficult for an unsuspecting employee to discern as fraudulent. The ability to guide victims through each step of the login and MFA process in a convincing manner highlights a significant leap in the technical maturity of cybercriminal operations.
Consequences: Data Exfiltration and Extortion Demands
Once an attacker successfully compromises an SSO account, the immediate objective is typically data exfiltration. With access to the victim’s SSO dashboard, the threat actors can enumerate and then access all connected applications and services that the compromised user account has privileges for. This could include sensitive customer databases, proprietary intellectual property, financial records, human resources information, and other critical business data. The scale of potential data theft is vast, limited only by the permissions of the compromised account.

Following the data exfiltration, the stolen information becomes leverage for extortion. Multiple organizations targeted in these vishing campaigns have reportedly received extortion demands signed by ShinyHunters. This direct communication, coupled with the evidence of data theft, strongly corroborates the group’s involvement. The extortion model typically involves demanding a ransom payment in cryptocurrency, threatening to publicly release the stolen data or sell it to other malicious actors on dark web forums if the demands are not met. The reputational damage, regulatory penalties, and legal liabilities associated with a public data breach often compel victim organizations to consider capitulating to these demands, creating a highly profitable criminal enterprise for groups like ShinyHunters.
Vendor and Industry Response
The targeting of major SSO providers like Okta, Microsoft Entra, and Google prompts significant concern across the cybersecurity industry. Okta, a prominent identity and access management provider, has responded by publishing a detailed report describing the advanced phishing kits employed in these voice-based attacks. This proactive communication from Okta serves to alert its customer base and the broader security community to the specific methodologies being used, enabling better defensive strategies.
In contrast, Microsoft has indicated that it has "nothing to share at this time," and Google has stated it has "no indication that Google itself or its products are affected by this campaign." These responses, while cautious, underscore the challenge for large platform providers in confirming or denying direct abuse of their systems when the attacks primarily target user credentials through social engineering rather than exploiting platform vulnerabilities. The attacks leverage the trust users place in these platforms, rather than inherent weaknesses in the SSO technology itself. The discrepancy in vendor responses highlights the complex nature of attributing and addressing social engineering attacks that exploit the human element rather than purely technical flaws.
ShinyHunters’ Targeting Strategy and Recent Activities
ShinyHunters has explicitly stated that Salesforce remains a primary interest, implying that access to customer relationship management (CRM) systems is a key objective, likely due to the wealth of customer and sales data they contain. The group also confirmed that they are leveraging data stolen in previous breaches, such as the widespread Salesforce data theft attacks, to identify and contact employees for their current vishing campaigns. This strategy exemplifies a common cybercriminal practice where previously acquired data, including phone numbers, job titles, names, and other personal details, is used to craft highly convincing and personalized social engineering calls. This level of reconnaissance significantly enhances the credibility of the impersonated IT support and increases the likelihood of a successful compromise.
Concurrently with these vishing operations, ShinyHunters has reactivated its Tor-based data leak site. The site currently lists several prominent organizations, including SoundCloud, Betterment, and Crunchbase, as recent breach victims. SoundCloud had previously disclosed a data breach in December 2023. Betterment confirmed this month that its email platform had been compromised and abused to send cryptocurrency scam emails, with data subsequently stolen. Notably, Crunchbase, a platform providing business information, had not publicly disclosed a breach until this recent listing by ShinyHunters. Crunchbase has since confirmed a cybersecurity incident involving the exfiltration of certain documents from their corporate network, emphasizing that business operations were not disrupted and that they have engaged cybersecurity experts and law enforcement. These revelations illustrate ShinyHunters’ ongoing commitment to data theft and their multi-faceted approach to monetization, extending from direct extortion to public data leaks.
Implications and Future Outlook
The resurgence of ShinyHunters with such sophisticated vishing tactics has profound implications for cybersecurity. It signals a critical shift in the threat landscape, where the human element is increasingly targeted as the weakest link, even when robust technical controls like MFA are in place. The success of these attacks underscores the imperative for organizations to implement comprehensive, multi-layered security strategies that address both technical vulnerabilities and human factors.
Looking ahead, it is highly probable that vishing and other forms of interactive social engineering will continue to proliferate. As technical defenses become more sophisticated, attackers will invariably pivot to exploit the most vulnerable component of any system: the human user. Organizations must therefore prioritize advanced security awareness training that specifically addresses real-time social engineering scenarios, including how to identify and report vishing attempts. Furthermore, the adoption of phishing-resistant MFA solutions, such as FIDO2 security keys or number-matching push notifications, can significantly mitigate the effectiveness of these attacks. Implementing a robust Zero Trust architecture, where no user or device is inherently trusted, can limit lateral movement even if an SSO account is compromised. Continuous monitoring, swift incident response capabilities, and proactive threat intelligence sharing are also critical for detecting and containing such advanced threats. The ongoing cat-and-mouse game between cybercriminals and cybersecurity defenders will undoubtedly see further innovations on both sides, making adaptive security postures and constant vigilance non-negotiable for enterprise resilience in the face of evolving cyber threats.