Newly unearthed internal documents, brought to light amidst a significant legal battle concerning child safety, suggest a deliberate and long-term strategy by Google to cultivate lifelong brand allegiance by embedding its products within the educational landscape. These revelations, originating from a November 2020 presentation, outline a vision for "onboarding" young learners into Google’s extensive ecosystem, with the explicit objective of fostering "brand trust and loyalty over their lifetime." This strategic approach, as previously reported by NBC News, appears to position educational institutions as crucial conduits for user acquisition and retention.
The unearthed documents, characterized by significant redactions, have emerged as part of a sprawling lawsuit involving numerous school districts, families, and state attorneys general. The core of this litigation accuses technology giants, including Google, Meta, ByteDance, and Snap, of developing and disseminating "addictive and dangerous" products that have demonstrably negatively impacted the mental well-being of young users. Notably, Snap has already reached a settlement in this complex legal arena.
Google’s investment in educational technology is not a recent development; the company has dedicated over a decade to developing and refining products tailored for classroom environments. This sustained effort has been instrumental in establishing Chromebooks as a ubiquitous presence in schools across the nation. The 2020 presentation further elaborates on this strategy, referencing studies that underscore the profound influence that laptop brands utilized in educational settings exert on subsequent consumer purchasing decisions. This suggests a calculated understanding that early exposure to a particular technological platform can significantly shape future consumer behavior.
Further examination of the documents reveals a consistent theme of early user engagement as a cornerstone of Google’s growth strategy. A particular slide prominently highlights a 2017 New York Times article, emphasizing a quote that articulates Google’s involvement in a competitive struggle to "hook students as future customers." This sentiment is repeatedly underscored within the presentation, with the assertion that "If you get someone on your operating system early, then you get that loyalty early, and potentially for life." This fundamental principle appears to guide Google’s educational outreach, extending beyond hardware to encompass software and content platforms.

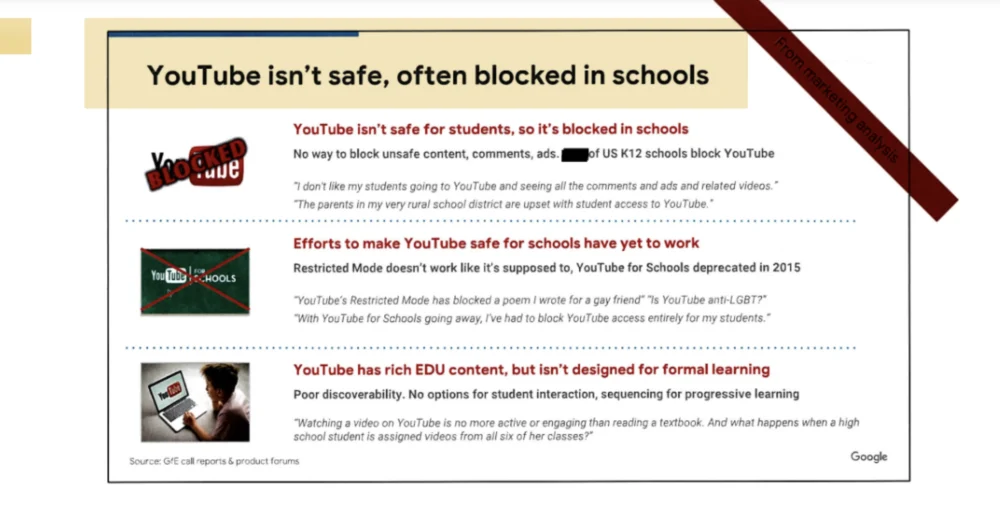
The documents also explore the potential of YouTube within educational contexts, suggesting that its integration could create a "pipeline of future users" and content creators. This points to a broader ambition of nurturing not only consumers but also active participants and contributors within Google’s digital universe. However, these internal discussions are not without introspection regarding the challenges and complexities of deploying YouTube in schools. Other slides acknowledge that the platform is "often blocked" by educational institutions, and that "efforts to make YouTube safe for schools have yet to work."
Moreover, the internal documentation candidly addresses the potential ramifications of YouTube’s widespread use on the mental health of young users. A 2024 presentation slide articulates a common user experience where individuals "regret time lost when they unintentionally ‘go down the rabbit hole,’" or that YouTube has "distracted" them from academic responsibilities and even disrupted essential sleep patterns. This acknowledgment, within Google’s own internal communications, adds a layer of complexity to the company’s educational initiatives, raising questions about the balance between user engagement and user well-being.
In response to these revelations, Google spokesperson Jack Malon issued a statement asserting that the documents "mischaracterize" the company’s endeavors. Malon emphasized that "YouTube does not market directly to schools and we have responded to meet the strong demand from educators for high-quality, curriculum-aligned content." He further clarified that "Administrators maintain full control over platform usage and YouTube requires schools to obtain parental consent before granting access to YouTube for students under 18."
The legal proceedings surrounding these accusations are ongoing, with jury selection for the social media addiction trial scheduled to commence on January 27th, 2026. This trial represents a critical juncture in the ongoing debate about the responsibilities of technology companies in safeguarding the well-being of young users and the ethical considerations surrounding the monetization of attention, particularly within educational environments.
The strategic deployment of educational technology by tech giants like Google is a complex phenomenon with far-reaching implications. The consistent presence of Chromebooks in classrooms, coupled with the integration of Google’s suite of productivity and content-sharing tools, creates an environment where students are habitually exposed to and proficient with Google’s operating systems and services from an early age. This early immersion can translate into a natural inclination to continue utilizing these platforms as they transition into higher education and professional life.

From a pedagogical perspective, the widespread adoption of Chromebooks has undoubtedly streamlined access to digital learning resources and facilitated collaborative projects. Educational institutions have benefited from the cost-effectiveness and ease of management associated with these devices. However, the internal documents suggest that this widespread adoption may be underpinned by a business strategy that prioritizes long-term customer acquisition over immediate pedagogical benefits. The "pipeline of future users" concept implies a proactive effort to shape consumer habits through early and sustained exposure.
The legal challenges highlight a growing societal concern regarding the addictive design of digital platforms and their potential impact on adolescent mental health. Allegations of exploiting vulnerabilities in young users for commercial gain are serious and underscore the need for greater transparency and accountability from technology companies. The fact that internal documents acknowledge the potential for distraction and regret associated with platforms like YouTube, while simultaneously pursuing their integration into educational settings, presents a significant ethical dilemma.
The broader market for educational technology is a substantial and growing one. Companies are increasingly recognizing the value of securing a foothold in this market, not only for revenue generation but also for establishing brand loyalty that can extend across a user’s lifetime. Google’s approach, as suggested by the internal documents, appears to be a sophisticated manifestation of this trend, leveraging the trust and familiarity built within the educational sphere to cultivate a generation of loyal consumers.
The long-term implications of this strategy are significant. If educational institutions become de facto marketing channels for technology companies, it raises questions about the independence and objectivity of educational technology choices. The potential for a symbiotic relationship, where educational needs align with corporate business objectives, warrants careful scrutiny. Furthermore, the emphasis on cultivating lifelong loyalty through early exposure could inadvertently stifle innovation and limit consumer choice in the future, as individuals may be less inclined to explore alternative platforms once deeply embedded within a particular ecosystem.
The future outlook for educational technology will likely be shaped by the outcomes of these legal battles and the evolving regulatory landscape. There is a growing demand for educational tools that are not only effective for learning but also designed with the well-being of young users at the forefront. Companies that can demonstrate a genuine commitment to ethical design and user safety, while also meeting the pedagogical needs of educators, will be best positioned for long-term success. Google’s challenge will be to navigate the complex intersection of its business objectives and its responsibilities as a provider of tools for young learners, ensuring that its educational initiatives genuinely serve the best interests of students.







