Google’s recent unveiling of an experimental "AI Inbox" for Gmail signals a significant departure from the traditional email interface, proposing a future where artificial intelligence curates and prioritizes incoming communications, potentially transforming how users interact with their digital mail. This innovative feature, currently in limited testing, moves away from the chronological list of messages, instead presenting users with an AI-generated overview of actionable items and topics requiring attention. While the long-term implications are substantial, early impressions suggest a powerful tool that may, for some, fundamentally alter their approach to inbox management, while others, accustomed to established personal systems, may find its current iteration less transformative.
The AI Inbox is positioned as an evolutionary step in Google’s ongoing integration of artificial intelligence into its core product suite. This initiative reflects a broader industry trend towards leveraging AI to streamline digital workflows and enhance user productivity. The concept behind AI Inbox is to distill the often overwhelming volume of emails into digestible, prioritized insights. Instead of requiring users to sift through individual messages, the AI attempts to identify key tasks, recurring themes, and important conversations, presenting them in a synthesized format. This approach aims to reduce cognitive load and enable users to focus on what truly matters, thereby reclaiming valuable time and mental energy.
At its nascent stage, the AI Inbox is accessible only to a select group of "trusted testers." This limited rollout strategy is typical for major technological advancements, allowing Google to gather crucial feedback, refine algorithms, and identify potential issues before a wider public release. It is important to note that the current functionality and user experience may not be representative of the final product. Furthermore, the initial implementation is restricted to consumer Gmail accounts, excluding Google Workspace users. This means that early evaluations are primarily based on personal email usage, which often differs in volume and nature from professional inboxes that can be significantly more demanding.

For individuals who have meticulously cultivated highly efficient email management systems, the introduction of AI Inbox presents an interesting case study. Many professionals and power users have developed sophisticated methods for achieving and maintaining an "inbox zero" philosophy – a state where the inbox is consistently cleared of messages, with each email either actioned, delegated, or archived. These systems often involve a deep understanding of personal workflow, rapid decision-making, and the strategic use of labels, filters, and archiving. The question arises whether an AI-driven system, designed for broader applicability, can genuinely enhance or even disrupt such finely tuned personal strategies.
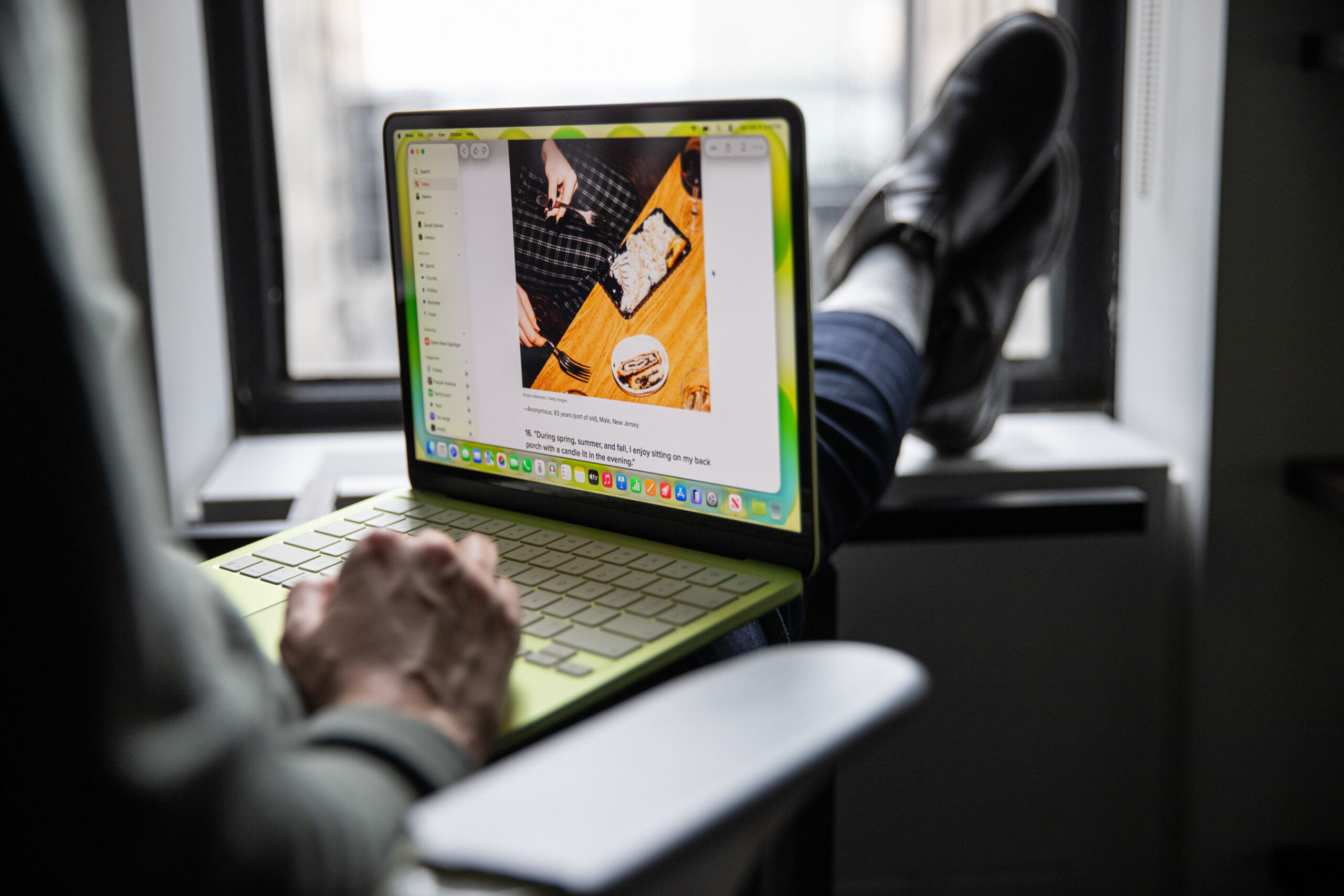
In its current form, the AI Inbox transforms the familiar linear display of emails into a dynamic, AI-curated dashboard. Upon activation, the interface shifts from a chronological list to a summary page. At the forefront are suggested to-do items, derived from the content of incoming and existing emails. These suggestions are often accompanied by direct links, allowing users to quickly access the relevant communication for further context or to formulate a response. Below the to-do list, the AI categorizes and presents "topics to catch up on," grouping related conversations and discussions. This thematic organization aims to provide a bird’s-eye view of ongoing matters without requiring users to recall specific sender names or subject lines.
A particularly noteworthy aspect of the AI Inbox’s initial output is its ability to surface items that have already been archived. This suggests that the AI is not solely operating on the current inbox but is analyzing a broader dataset of user communication. In one observed instance, archived conversations concerning tax preparation and toddler potty training were highlighted. While this demonstrates the AI’s capacity to identify potentially important threads, it also raises questions about its understanding of user intent and the context of archived information. For individuals who archive emails precisely because they are no longer immediately actionable or require active management, the re-emergence of these items in a prioritized view might be perceived as an intrusion or a misinterpretation of their organizational strategy.
The AI Inbox’s approach can be analogized to Google Search’s AI Mode, where the search engine synthesizes information to provide direct answers and summaries rather than just links. However, applying this to the personal and often sensitive realm of email introduces unique challenges. The effectiveness of such a system hinges on the AI’s ability to accurately discern relevance and urgency from a user’s perspective. For users who have spent years developing a personalized system for managing their digital communications, an AI that presents what it thinks is important, rather than what the user has explicitly designated as such, can feel counterproductive. The AI Inbox’s tendency to populate the screen with what it deems necessary, even if it requires scrolling on a standard display, contrasts sharply with the minimalist, action-oriented approach of a meticulously organized inbox.

The core tension lies in the AI’s presumptive nature versus a user’s deliberate organizational strategy. If a user has a system that prioritizes immediate action and then archives, the AI’s surfacing of archived items, even if relevant to broader life topics, might be seen as an unnecessary distraction. The AI’s interpretation of "what’s relevant right now" may not align with the user’s specific workflow, particularly if that workflow involves a clear delineation between active tasks and background considerations. For instance, ongoing family discussions about important life events, while significant, might not require immediate AI-driven attention if they are being actively managed through other means.
However, the AI Inbox holds considerable promise for users who do not maintain such stringent organizational habits. For individuals who find their inboxes overflowing with unread messages and struggle to identify priorities, the AI’s nudges and suggestions could prove invaluable. Google’s Vice President of Product for Gmail, Blake Barnes, has indicated that the company views AI Inbox as a complementary tool, designed to enhance, rather than replace, existing email workflows. This perspective suggests that the AI is intended to act as an intelligent assistant, augmenting the user’s ability to navigate their inbox, particularly for those who may not have developed advanced personal management techniques.
Google is actively investing in the evolution of AI Inbox, with plans for significant feature enhancements. These potential additions aim to bolster its utility and integration into daily life. Proposals include the ability to mark AI-suggested items as completed, a critical step for reinforcing the system’s action-oriented nature. The integration of quick-reply buttons directly within AI Inbox suggestions could further streamline responses. More ambitiously, Google is exploring the possibility of pre-drafting replies, even suggesting meeting times in conjunction with Google Calendar integration, transforming AI Inbox into a proactive scheduling assistant. The concept of users instructing the AI to proactively monitor communications from specific individuals underscores a vision of a deeply personalized and responsive digital assistant.
If these ambitious plans are realized, Gmail could transition from a repository of incoming messages requiring constant attention to an intelligent personal assistant. This AI-supercharged model could significantly alter how individuals manage their digital lives, especially for those who rely heavily on email for professional and personal coordination. Such a transformation, however, places a considerable degree of trust in Google’s AI capabilities. Users would be entrusting the AI with the responsibility of managing crucial aspects of their communication and potentially their schedules, shifting the burden of system design from the individual to the technology.

The rapid expansion of AI Mode in Google Search provides a precedent for how quickly AI Inbox might evolve and become more integrated into user workflows. While the current iteration may not resonate with individuals who have long-established and effective personal email management systems, its potential for growth is undeniable. The learning curve and the user’s evolving relationship with the AI will undoubtedly influence its long-term adoption. As with any nascent technology, the initial assessment may not capture the full scope of its future capabilities. However, for now, the AI Inbox represents a bold experiment in redefining the fundamental interaction with one of the internet’s most ubiquitous tools, offering a glimpse into a future where artificial intelligence plays an even more central role in organizing our digital existence.