Google is initiating a significant transformation of its ubiquitous Gmail platform, integrating advanced artificial intelligence capabilities powered by its Gemini model directly into the user experience. This strategic evolution introduces new functionalities, notably "AI Overviews" and "AI Inbox," designed to fundamentally redefine email management by addressing the escalating volume of digital correspondence. Central to this ambitious rollout is a steadfast commitment from Google: an explicit assurance that user emails and their content will not be leveraged to train the underlying AI models, a crucial declaration intended to mitigate prevalent concerns regarding data privacy and security.
Since its inception in 2004, email has evolved from a novel communication tool into an indispensable, yet often overwhelming, daily fixture for billions globally. The digital landscape has fundamentally shifted, characterized by an exponential increase in the sheer volume of information vying for attention. Users are routinely confronted with hundreds, if not thousands, of emails weekly, ranging from critical business communications and personal correspondence to marketing solicitations and automated notifications. This relentless influx has created a significant cognitive burden, transforming the once-efficient inbox into a source of stress and diminished productivity. Google’s latest initiative with Gemini integration is a direct response to this contemporary challenge, aiming to restore efficacy and ease to the email experience by intelligently filtering, summarizing, and prioritizing information.
The Genesis of AI Overviews: Streamlining Information Access
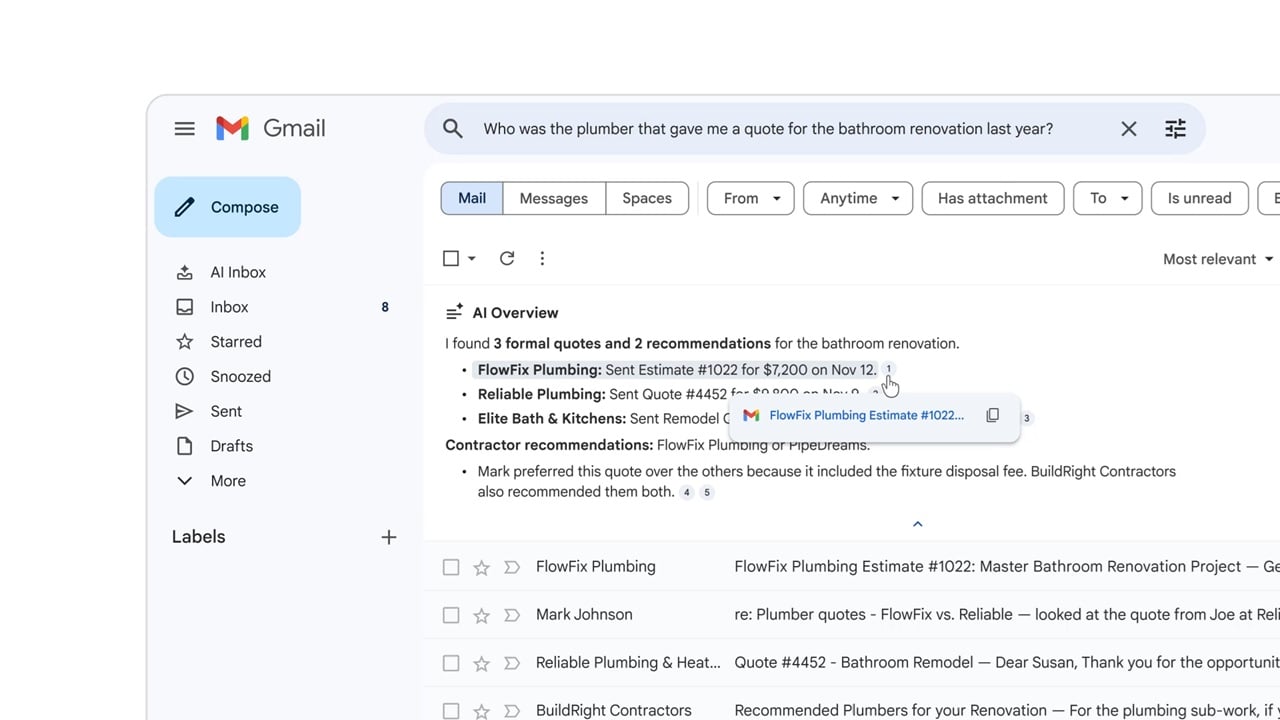
One of the cornerstone features of this new era in Gmail is "AI Overviews." This functionality is engineered to tackle the pervasive problem of information overload within email threads. In corporate environments particularly, email conversations can span numerous messages, accumulate complex histories, and often require extensive sifting to extract critical details or understand context. AI Overviews provides a succinct, contextually relevant summary of these lengthy exchanges. By employing sophisticated natural language processing (NLP) and large language models (LLMs), the system can distill the essence of a conversation, highlight key decisions, action items, and relevant participants, thereby presenting users with an immediate, condensed understanding without requiring them to manually parse every preceding message.

This feature represents a paradigm shift from traditional keyword-based search within an email client. Instead of merely locating messages containing specific terms, AI Overviews actively comprehends the semantic content of the thread, synthesizing information into an actionable summary. This capability is poised to significantly reduce the time spent on email triage, allowing professionals to quickly grasp the status of projects, understand client interactions, or catch up on internal discussions with unprecedented efficiency. Google’s decision to roll out AI Overviews to all users at no additional cost underscores its commitment to democratizing advanced productivity tools, ensuring a broad impact across its user base.
Introducing the AI Inbox: A Personalized Command Center
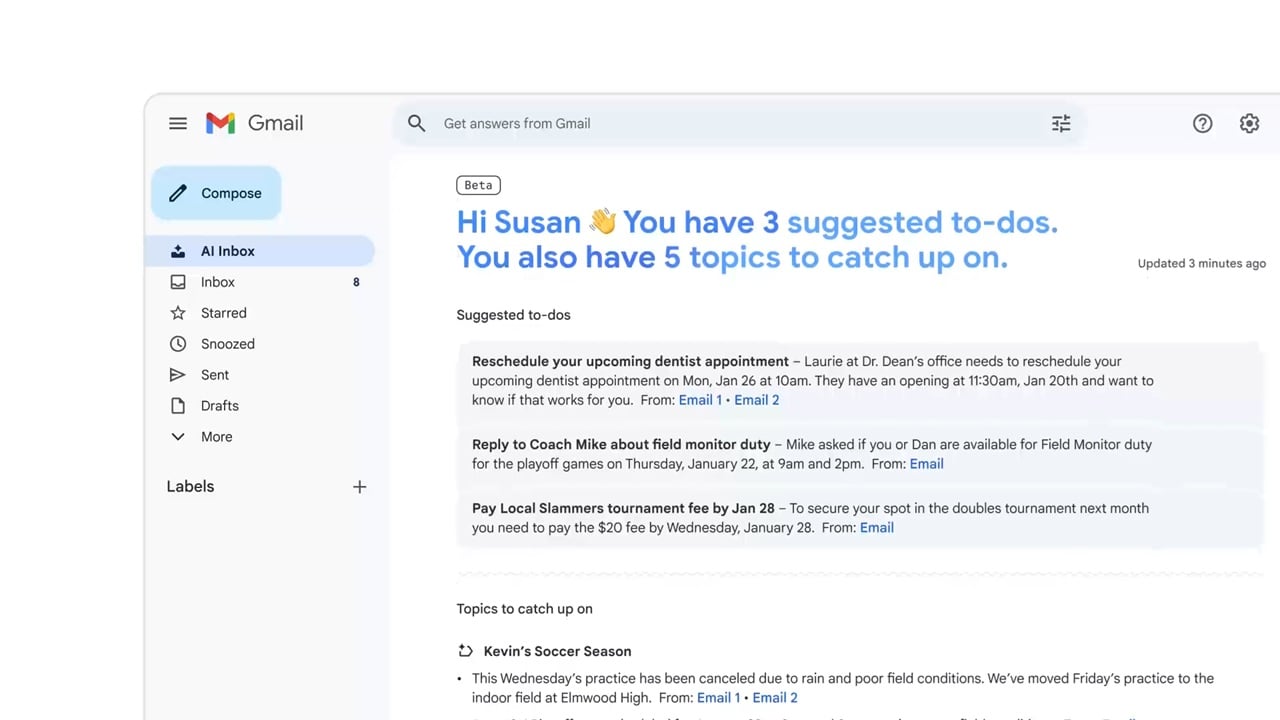
Beyond the reactive summarization offered by AI Overviews, Google is introducing a more proactive and personalized layer of intelligence through the "AI Inbox." Positioned prominently above the traditional inbox on the left sidebar, this new section functions as a dynamic, personalized briefing module. Its purpose is to elevate the most pertinent information, identify critical tasks, and provide a rapid overview of what demands immediate attention.
The AI Inbox leverages Gemini to act as a highly intelligent personal assistant, capable of discerning "Very Important Persons" (VIPs) within a user’s network. This prioritization is not based on static contact lists alone but is dynamically inferred through a multitude of signals, including email frequency, existing contacts, and sophisticated analysis of message content to deduce professional or personal relationships. By identifying these key individuals and their communications, the AI Inbox ensures that messages from critical contacts are highlighted, preventing them from being buried under less urgent correspondence.

Furthermore, the AI Inbox is designed to identify and surface actionable items embedded within emails. Whether it’s a deadline mentioned in a project update, a meeting request from a collaborator, or a query requiring a response, the system aims to present these tasks clearly, transforming the passive act of receiving email into an active management process. This shift from a purely chronological or category-based inbox to an intelligently prioritized one represents a significant leap towards truly smart email management. However, access to this advanced AI Inbox feature is initially exclusive to users with Google AI Pro and Ultra subscriptions in the United States, signaling a tiered approach to the deployment of premium AI functionalities.
The Cornerstone of Trust: Google’s Data Privacy Commitment
Perhaps the most critical aspect of this entire rollout, and one that Google has proactively emphasized, is its explicit pledge regarding user data: the company will not utilize personal emails or their content to train its foundational AI models. This commitment directly addresses the growing global apprehension surrounding artificial intelligence and user privacy. As AI systems become increasingly sophisticated and integrated into everyday tools, concerns about how personal data is collected, processed, and used for model training have escalated. Users are understandably wary of their sensitive communications potentially contributing to a vast dataset that could inadvertently reveal private information or be exploited.
Google’s assurance is a strategic move to build and maintain user trust in an era where data privacy breaches and algorithmic biases are frequent headlines. It positions these new AI features as tools designed solely for user benefit and productivity enhancement, rather than as mechanisms for data harvesting. While the technical specifics of how this isolation is achieved are not fully detailed, such a promise typically implies robust data governance policies, potentially involving on-device processing for certain features, strict anonymization protocols, or the implementation of differential privacy techniques. The ability for users to toggle off these AI features further reinforces a user-centric approach to data control and autonomy.
This stance is particularly significant in the broader context of AI development, where large language models typically require vast quantities of data for effective training. Google’s commitment suggests a clear delineation between the data used for general model development and the proprietary, sensitive data contained within individual user accounts. It seeks to assure users that their personal communications remain private, even as AI algorithms analyze them in real-time to generate summaries or prioritize messages.
Broader Implications and the Evolving Productivity Landscape
The integration of Gemini into Gmail is not an isolated development but rather a significant marker in the ongoing evolution of digital productivity tools. This move positions Gmail at the forefront of AI-powered communication, setting a new benchmark for competitors in the email client and broader workspace software markets. Companies like Microsoft, with their Copilot integration in Outlook, are also heavily investing in similar AI augmentation, creating a competitive landscape where intelligent assistance is rapidly becoming a standard expectation rather than a premium add-on.
This shift has profound implications for user behavior and enterprise adoption. For individual users, the promise is a liberation from the tyranny of the inbox, allowing for greater focus on high-value tasks. For businesses, the potential for increased efficiency, faster information dissemination, and reduced communication overhead could translate into tangible productivity gains. However, the adoption curve will likely be influenced by the accuracy of the AI, the perceived value of the premium features, and, crucially, sustained trust in Google’s privacy pledges.
Challenges remain, particularly concerning the inherent limitations of current LLMs, such as the potential for "hallucinations" or misinterpretations of complex or nuanced content. While AI Overviews and AI Inbox are designed to be assistive, an over-reliance on automated summaries without critical review could lead to missed details or misunderstandings. Therefore, user education on responsible AI interaction will be paramount. Furthermore, the tiered access model for the AI Inbox raises questions about equitable access to advanced productivity features, potentially creating a digital divide between subscribers and non-subscribers.
Future Outlook: Towards a More Intelligent Digital Ecosystem
Looking ahead, Google’s integration of Gemini into Gmail is likely just the beginning of a much broader strategy to infuse AI across its entire suite of products. One can anticipate further enhancements in personalization, predictive capabilities, and cross-platform integration. Imagine AI that not only summarizes emails but proactively drafts responses based on context, schedules meetings automatically, or even anticipates user needs across different Google Workspace applications, from Docs to Calendar.
The ultimate vision appears to be a seamlessly integrated AI assistant that operates across all digital touchpoints, learning and adapting to individual user preferences and workflows. This proactive, context-aware intelligence could fundamentally alter how individuals interact with their digital environments, moving towards a future where technology anticipates and facilitates human action more intuitively. However, the success of this ambitious trajectory will hinge on Google’s ability to consistently deliver on its promises of performance, utility, and, above all, unwavering commitment to user privacy and data security in an increasingly AI-driven world. The ethical considerations and regulatory landscape surrounding AI will continue to evolve, demanding constant vigilance and adaptability from technology providers as they push the boundaries of intelligent assistance.







