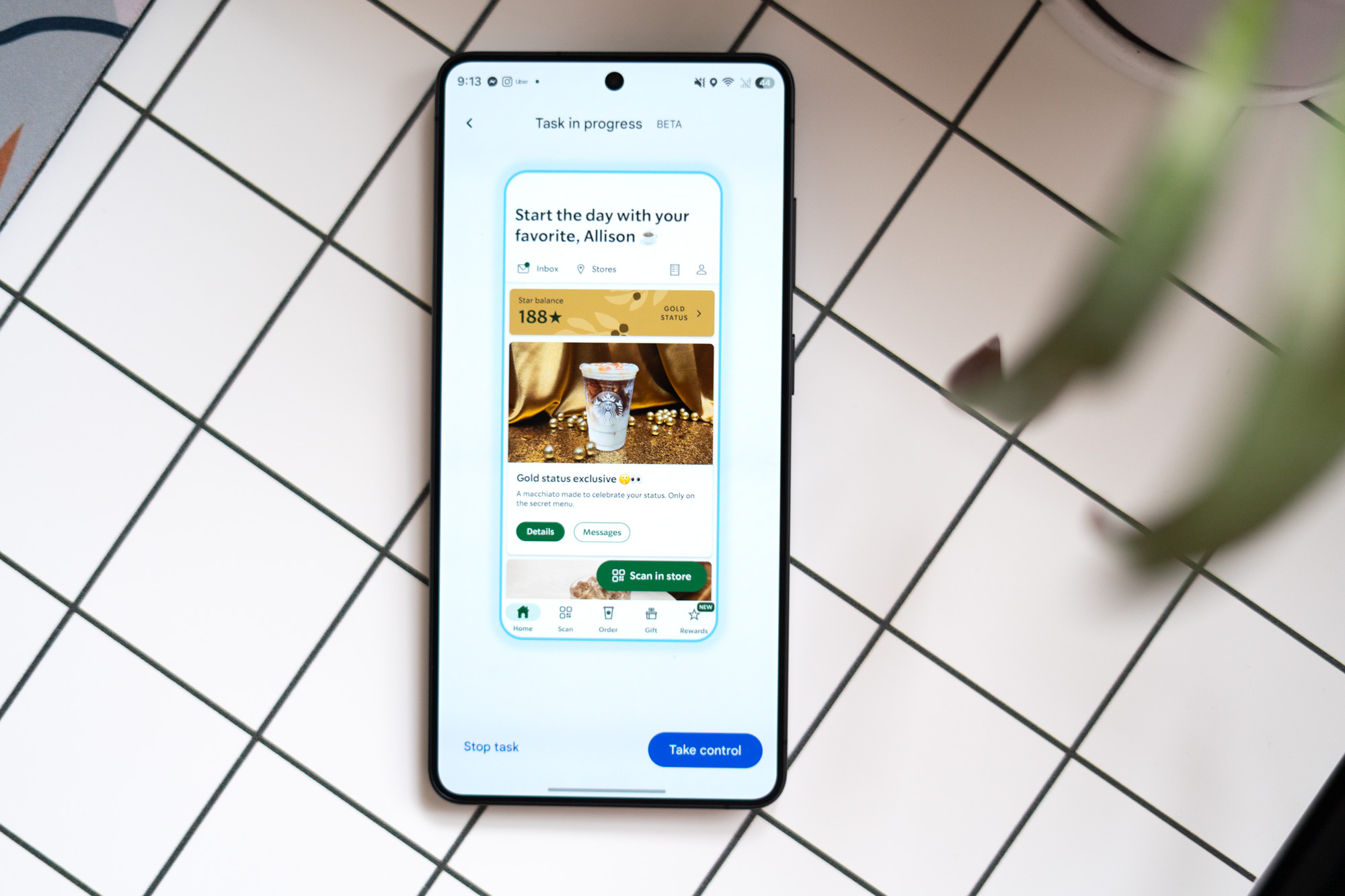
The year 2025 marked a significant turning point for the entertainment industry, as Hollywood’s engagement with artificial intelligence, particularly generative AI, moved beyond the realm of niche post-production tools to become a central focus of studio strategies, yet the promised revolution largely failed to materialize, leaving a landscape littered with uninspired projects and growing industry unease. While AI has long been a quiet collaborator in film and television, assisting with tasks like de-aging actors or digitally removing green screens, this was the year studios aggressively pursued generative AI capable of creating entirely new content from textual prompts. This pivot, however, yielded little beyond what has been characterized as derivative and uninspired output, failing to justify the considerable investment and industry attention it garnered.
The burgeoning relationship between Hollywood and generative AI was not without its initial friction. The very foundation of many generative AI models—their training data—raised immediate legal questions, as studios like Disney, Universal, and Warner Bros. Discovery initiated lawsuits alleging copyright infringement. These legal challenges posited that these AI systems had learned by analyzing vast quantities of protected intellectual property without proper authorization. However, instead of pursuing a path of aggressive litigation to curb the unchecked proliferation of these technologies, a notable shift occurred: major industry players began forging strategic alliances with the very AI companies they had previously challenged. This unexpected convergence signals a new phase of generative AI integration, one that, based on early indicators, is poised to introduce a significant degree of creative dilution into the entertainment sphere.
The generative AI landscape in 2025 was populated by both established tech giants and emerging startups, all vying for a stake in Hollywood’s lucrative ecosystem. Industry titans such as Google and OpenAI continued to dominate headlines with their advanced AI capabilities. Concurrently, smaller entities like Asteria, a startup championed by Natasha Lyonne and focused on developing film projects through "ethically engineered" video generation, and Showrunner, an Amazon-backed platform enabling users to generate animated "shows" from simple text prompts via Discord, emerged with ambitious claims. These newer companies were particularly eager to position their generative AI solutions as catalysts for accelerating film and television development while simultaneously promising substantial reductions in production costs.
Despite the fanfare, the tangible outcomes from these ventures proved largely underwhelming. Asteria, for instance, offered little beyond aspirational pronouncements following the announcement of its inaugural film project, leaving the public unconvinced of its purported groundbreaking potential. Similarly, the output from Showrunner, characterized by its crudely assembled and derivative animation, struggled to inspire confidence in its ability to captivate a broad audience or justify its subscription model. The underlying objective for platforms like Showrunner appeared to be less about empowering individual creators and more about securing lucrative partnerships with established studios. The aspiration was to embed their technology into existing studio platforms, enabling the creation of bespoke content featuring iconic characters from beloved franchises, a concept that, at its inception, seemed preposterous given the rudimentary quality of their generative output.
The notion of integrating such low-fidelity generative AI into established franchises seemed far-fetched when platforms like Showrunner first entered the market, producing content akin to amateurish digital parodies. Yet, the industry’s trajectory shifted dramatically when Disney signaled its willingness to explore the potential of such generative tools, despite their inherent limitations in producing anything beyond fleeting digital memes. In a move that reverberated across the industry, Disney inked a three-year licensing agreement with OpenAI, valued at one billion dollars. This landmark deal grants Sora users the ability to generate AI-driven videos featuring a catalog of 200 characters drawn from the Star Wars and Marvel universes, among others.

Netflix emerged as another early adopter, openly embracing generative AI by integrating it into its production pipeline. Following its initial application of the technology for special effects in an original series, the streaming giant published a comprehensive set of guidelines for its partners, encouraging them to explore generative AI solutions. While not mandating its use, Netflix clearly articulated its interest in leveraging generative AI to achieve significant cost savings in visual effects production. This trend was quickly mirrored by Amazon, which released several Japanese anime series that suffered from demonstrably poor localization. The dubbing process for these series notably excluded human translators and voice actors, resulting in a subpar viewing experience.
Amazon’s generative AI-dubbed anime became a stark illustration of the technology’s shortcomings and highlighted a concerning trend among some studios: a perceived lack of rigor in ensuring the quality and polish of AI-generated content before its public release. This was further underscored by Amazon’s machine-generated television recaps for its Prime Video service, which frequently contained factual inaccuracies regarding show plots. The swift withdrawal of both the AI-dubbed series and the recap feature suggested a realization on Amazon’s part that audiences would indeed notice and be critical of such inconsistent and low-quality outputs. However, the company offered no definitive assurance against similar future endeavors.
Beyond these prominent examples, a series of less impactful initiatives, such as the emergence of AI-generated "actresses" like Tilly Norwood, contributed to a growing perception that segments of the entertainment industry were attempting to prematurely push generative AI-created content onto consumers. This approach left many audiences unimpressed and alienated, failing to demonstrate any compelling reason for public enthusiasm beyond the cost-saving motivations of industry executives and their staunch supporters. The year concluded with a scarcity of projects that truly showcased the transformative potential of generative AI, leaving many to question its true value proposition for creators and audiences alike.
While the full ramifications of collaborations like Disney’s partnership with OpenAI are still unfolding, AI’s presence in Hollywood is poised for further amplification. Disney has announced plans to dedicate a significant portion of its streaming service to user-generated content sourced from Sora, and it intends to encourage its workforce to utilize OpenAI’s ChatGPT products. The overarching significance of the Disney-OpenAI deal lies in the signal it sends to other studios, potentially ushering in a new era characterized by the widespread adoption of generative AI, irrespective of its creative merits.
Regardless of its ultimate success or failure, Disney’s strategic move underscores a desire to remain competitive in an evolving technological landscape. This decision prompts other production houses to consider similar AI integration, raising concerns about the potential for an escalating influx of AI-generated content across the entertainment spectrum, much of which may prove to be of questionable artistic merit. The industry appears to be navigating a precarious transition, where the allure of technological advancement and potential cost efficiencies may overshadow the fundamental principles of creative excellence and audience engagement. The coming years will likely reveal the long-term consequences of this accelerated embrace of generative AI, determining whether it becomes a truly valuable tool or a persistent source of creative stagnation.