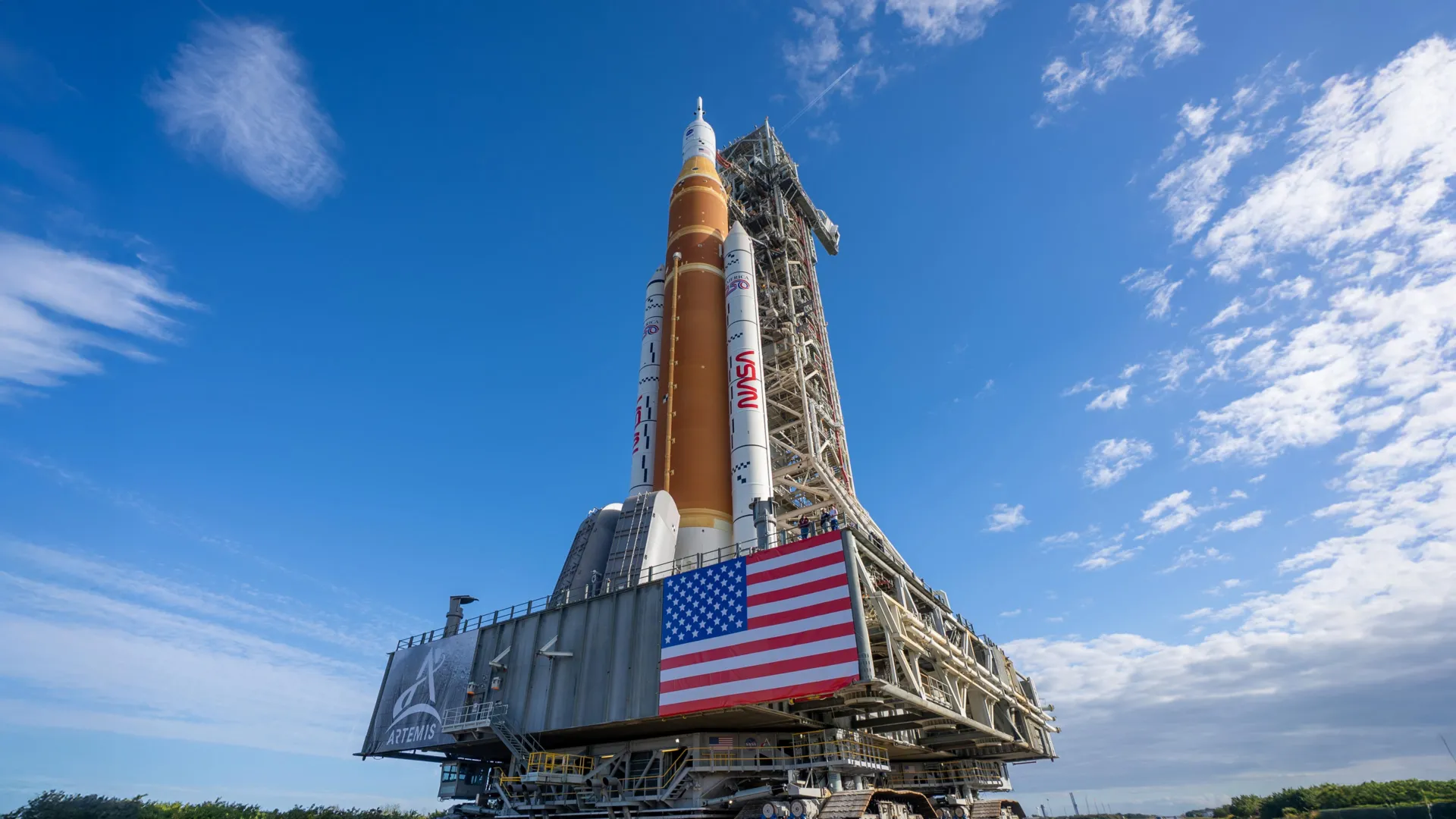
Following a period of profound strategic reorientation and substantial investment, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is poised to embark on a pivotal mission, dispatching astronauts on an orbital journey around the Moon for the first time in over half a century. This forthcoming expedition, designated Artemis II, represents a critical precursor to establishing a sustained human presence on the lunar surface, signaling an intensified era of American leadership in space exploration and scientific discovery, underpinned by robust national policy and significant fiscal allocations through legislative initiatives such as the Working Families Tax Cut Act.
The trajectory of U.S. space endeavors has undergone a notable transformation over recent years, with the agency’s mandate progressively refined to align with an overarching national space policy. This updated directive has consistently emphasized the imperative of American preeminence across the celestial domain, concurrently accelerating advancements in exploration, scientific understanding, and technological innovation. With a discernible focus on deep-space human spaceflight capabilities, fostering research excellence, and augmenting national capacities, NASA is reportedly executing its multifaceted programs with revitalized purpose and enhanced operational tempo.
Foundational Pillars of a New Space Era
The current momentum within NASA is not an isolated phenomenon but rather the culmination of foundational strategic actions initiated during the preceding administration. During this period, several landmark developments reshaped the landscape of American space enterprise. Crucially, the United States established the U.S. Space Force, an independent branch of the armed forces dedicated to protecting U.S. interests in space. Concurrently, the ambitious Artemis campaign was inaugurated, aiming to return humans to the Moon, and the Artemis Accords were introduced. These accords, a set of non-binding principles designed to guide civil space exploration and foster responsible behavior in space, have garnered substantial international support, with a growing consortium of over 60 nations now signatories, underscoring a multilateral commitment to a shared vision for lunar and deep-space activities. Furthermore, this era marked the triumphant resumption of American astronaut launches from U.S. soil, a critical milestone that restored domestic human spaceflight capabilities after a hiatus following the conclusion of the Space Shuttle program, largely facilitated by innovative public-private partnerships.
With a meticulously articulated National Space Policy now firmly in place, complemented by the comprehensive funding framework provided by the Working Families Tax Cut Act, NASA asserts it possesses the requisite strategic guidance, financial resources, and statutory authority essential for prosecuting its ambitious, long-term strategic objectives. This integrated approach signifies a departure from ad-hoc project-based funding, establishing a more stable and predictable environment for complex, multi-decade initiatives.
Accelerated Progress Across Diverse Domains
The initial year of the current administrative term has witnessed a surge in operational outputs and developmental progress across NASA’s broad portfolio. Within this twelve-month span, the agency successfully executed two crewed space missions, demonstrating continued proficiency in human spaceflight operations. In the realm of scientific inquiry, a remarkable 15 new science missions were launched, signifying a sustained commitment to expanding humanity’s knowledge base across various disciplines, from astrophysics to Earth observation. A significant technological advancement was also achieved with the successful test flight of a novel experimental X-plane, pushing the boundaries of aeronautical design and performance.
Beyond these tangible achievements, accelerated development has been observed across a spectrum of critical priorities. Lunar exploration efforts are progressing rapidly, laying the groundwork for future sustained presence. Earth science initiatives continue to yield vital data on climate change and environmental dynamics. Planetary defense programs are advancing, enhancing the nation’s capacity to detect and mitigate potential celestial threats. Next-generation aeronautics research is exploring groundbreaking concepts for future air travel and atmospheric flight. Concurrently, a focused effort is underway to develop advanced technologies specifically tailored to support forthcoming human missions to Mars, positioning the agency for eventual interplanetary travel.
Central to this accelerated agenda is the meticulous preparation for the aforementioned Artemis II mission. This mission, designed to ferry astronauts around the Moon, serves as an indispensable proving ground for the systems, procedures, and human factors involved in deeper space exploration. It is meticulously engineered to validate the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in a crewed flight environment beyond low-Earth orbit, a crucial step before any attempts at lunar landing. Agency leadership emphasizes that these accomplishments are a direct consequence of fostering a workforce environment that actively encourages rapid progress, the pursuit of audacious objectives, and the consistent delivery of measurable, tangible outcomes.
Strategic Vision and Unprecedented Momentum
In a recent articulation of the agency’s direction, NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman underscored the clarity, purpose, and accelerated momentum that have characterized NASA’s operations under the current administration. He highlighted the President’s vision as a catalyst for American leadership in space, emphasizing a reinforced focus on human spaceflight and the imminent deep-space exploration by NASA astronauts, marking a return to such ventures after more than five decades. The Administrator posited that the executive direction provided has been unparalleled since the era of President John F. Kennedy, attributing the sharpened mission focus, aligned priorities, and empowered workforce directly to this leadership. This strategic clarity has reportedly enabled NASA to move with greater agility and conceptual ambition, confidently advancing a future predicated on American superiority in the space domain for generations to come.
This renewed executive emphasis is perceived within analytical circles as providing a crucial long-term stability that can be elusive in government-funded initiatives. The consistent articulation of goals and the provision of dedicated resources through legislative acts like the Working Families Tax Cut Act allow for sustained development cycles, critical for projects with inherent multi-decade timelines, such as deep-space exploration and lunar infrastructure development. This contrasts with periods of less defined policy, which can lead to project cancellations or significant delays due to shifting political priorities or budget uncertainties.
Charting the Future: Lunar Bases, Scientific Frontiers, and Interplanetary Travel
Looking ahead, NASA officials convey a strong sense of preparedness to further build upon the agency’s recent achievements. Under the continued leadership, a definitive objective has been set for American astronauts to return to the lunar surface by 2028. This return is envisioned not as a transient visit but as the initial phase of establishing a permanent, long-term human presence supported by a fully operational lunar base. This ambitious undertaking necessitates the development of advanced habitats, in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) technologies, and robust logistics chains to sustain human life and scientific operations in the challenging lunar environment.
Beyond human exploration, NASA’s commitment to scientific discovery remains unwavering. The agency will continue to launch and operate a diverse array of science and discovery missions. A prominent milestone anticipated before the year’s end is the operational deployment of the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope. This cutting-edge observatory is designed to conduct wide-field surveys of the cosmos, providing unprecedented insights into dark energy, exoplanet populations, and general astrophysics, promising to revolutionize our understanding of the universe.
In a forward-looking strategy to enable future deep-space exploration beyond the Earth-Moon system, NASA is aggressively advancing research and development in nuclear power and propulsion technologies. These revolutionary systems are deemed essential for expanding mission capabilities, drastically reducing transit times, and enabling the exploration of the outer reaches of the solar system, including potential human missions to Mars and beyond. Concepts such as nuclear thermal propulsion (NTP) and nuclear electric propulsion (NEP) offer significant advantages over conventional chemical rockets, providing higher thrust-to-weight ratios or greater specific impulse, thereby reducing mission durations and payload mass requirements.
As NASA transitions into the second year of the current administrative term, it does so with a clearly articulated mission, a highly motivated and expanding workforce, and a robust network of strategic partnerships encompassing both commercial industry and international allies. The agency’s focus remains steadfast on extending American leadership in the complex and competitive domain of space, simultaneously pursuing transformative discoveries that possess the potential to profoundly influence humanity’s future trajectory for generations to come. This integrated approach, combining governmental strategic direction with commercial agility and international cooperation, positions the United States at the vanguard of a new era of space exploration and utilization, one that promises not only scientific advancement but also geopolitical influence and economic opportunity across the cosmos. The upcoming Artemis II mission, therefore, is not merely a circumlunar flight; it is a profound declaration of intent, signaling the commencement of humanity’s sustained return to its celestial neighbor and the subsequent expansion into the broader solar system.